Figure 3.
Active ERK2 Interacts with KLF4 Initiating KLF4 Nuclear Export
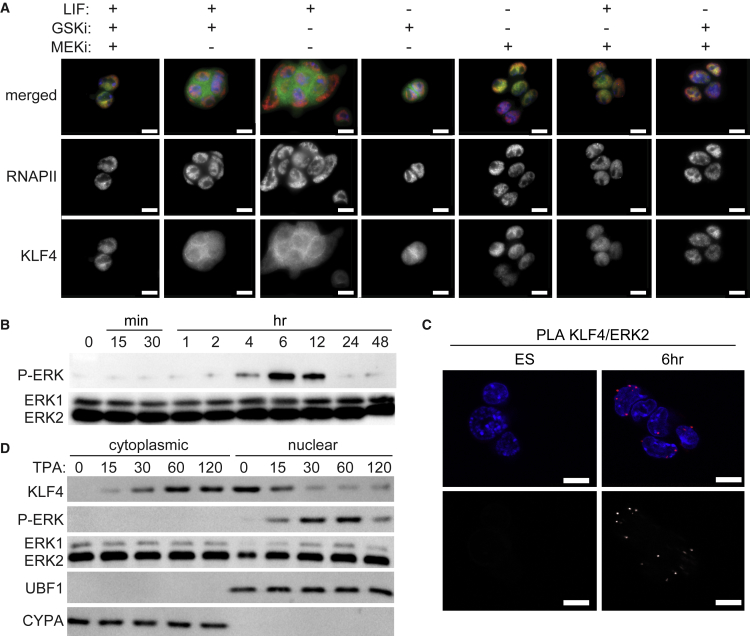
(A) Immunofluorescence images of ESCs cultured for 6 hr with the indicated components: LIF, MEKi (MEK1 inhibitor, PD0325901), and GSKi (GSK3 inhibitor, CHIR99021). Merged images display KLF4 in green, RNAPII-S5P in red, and DAPI in blue. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(B) Immunoblot for activated ERK1/2 (pTEpY) and total ERK1/2 in ESCs cultured with LIF/2i (0), 15 and 30 min, 1, 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, and 48 hr after LIF/2i removal.
(C) Proximity ligation amplification (PLA) for KLF4/ERK2 displays the interaction between ERK2 and KLF4 6 hr after LIF/2i withdrawal but not in ESCs maintained in LIF/2i. Images shown are single optical sections. Merged images display DAPI in blue and PLA in red. Bottom images display grayscale PLA signal. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(D) Immunoblot for ESCs treated with TPA and sampled at the indicated time in minutes. With TPA treatment, ERK phosphorylation and KLF4 nuclear export occur more rapidly starting at 15 min. Cyclophilin A (CYPA) and the nucleolar protein upstream binding factor (UBF1) reveal purity of the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively.
See also Figure S3.