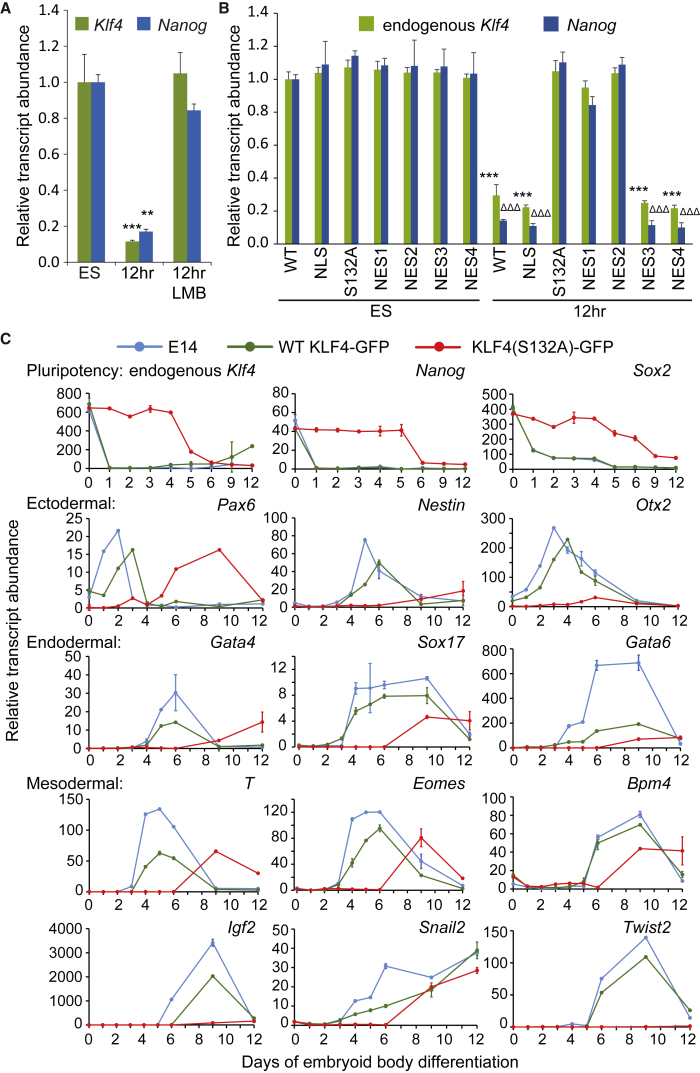
Figure 6.
KLF4 Nuclear Export Inhibition Delays Exit from Naive Pluripotency and Differentiation of Embryoid Bodies
(A) Treatment with 5 μg/mL LMB prevents downregulation in Klf4 and Nanog transcripts that normally occurs 12 hr after LIF/2i withdrawal. Average data from three biological replicates are normalized to levels observed in undifferentiated ESCs. Statistical differences are indicated by ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Error bars represent standard deviation.
(B) Expression of endogenous Klf4 and Nanog is maintained after 12 hr of differentiation in KLF4(S132A)-GFP, KLF4(NES1)-GFP, and KLF4(NES2)-GFP mutants but not in wild-type (WT) KLF4-GFP, KLF4(NLS)-GFP, KLF4(NES3)-GFP, and KLF4(NES4)-GFP mutants. Average data from three biological replicates are normalized to the levels observed in undifferentiated ESCs expressing WT KLF4-GFP. Statistical differences from the undifferentiated ESC levels for endogenous Klf4 transcript levels are indicated by ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and Nanog transcript levels are indicated by ΔΔΔp < 0.001. Error bars represent standard deviation.
(C) Relative gene expression analysis for pluripotency and germ layer markers in untransfected ESCs (E14), WT KLF4-GFP, and KLF4(S132A)-GFP transfected ESCs differentiated to embryoid bodies for 12 days reveals that expression of KLF4(S132A)-GFP delays ESC differentiation. Data shown are averages of three qRT-PCR replicates for each time point. Error bars represent standard deviation.
See also Figure S6.