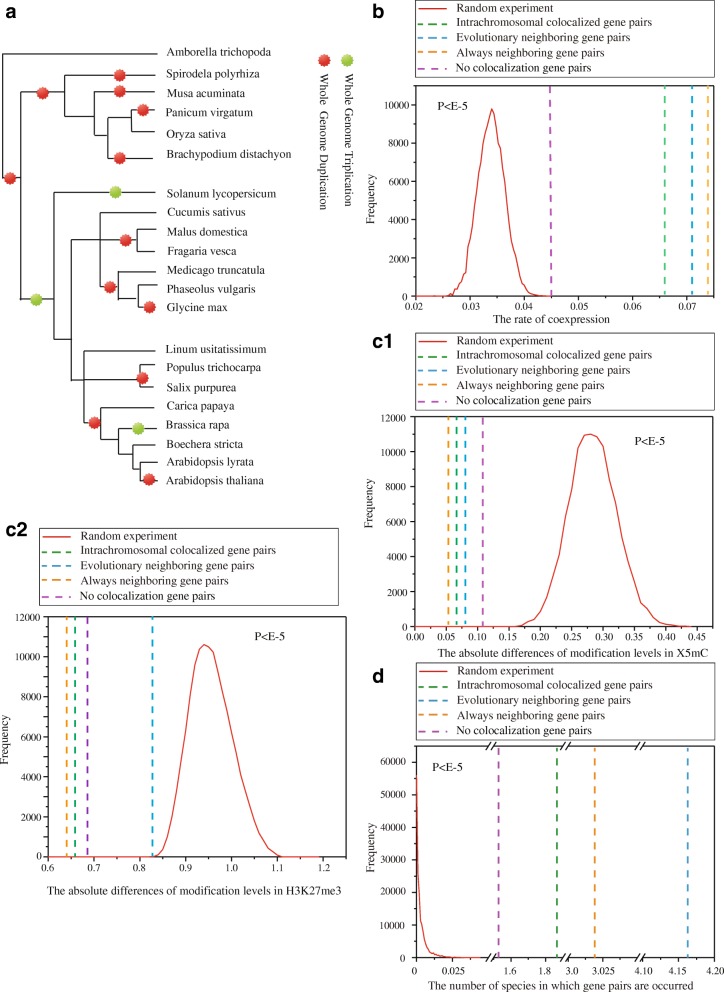
Fig. 1.
Different types of colocalized genes differentially contribute to co-expression, co-modification and conservation across species. a A phylogeny of species included in this study (partly adapted from [27]). Whole genome duplication and triplication events are marked according to the Plant Genome Duplication Database (PGDD) [28, 29]. b The frequency of co-expressed gene pairs of three colocalized gene pairs and no-colocalized genes in threshold 0.5. c1 and c2 The absolute difference in the modification levels of histone X5mC and H3K27me3, respectively, in three colocalized gene pairs and no-colocalized genes. d The number of species in which gene pairs of the three colocalizations and no-colocalizations are found. The red curves show the frequency distributions for 10,000 permuted randomizations of the same number of pairs as in the real data. Error bars were calculated by bootstrapping. Significance values calculated from the Mann–Whitney U test are shown