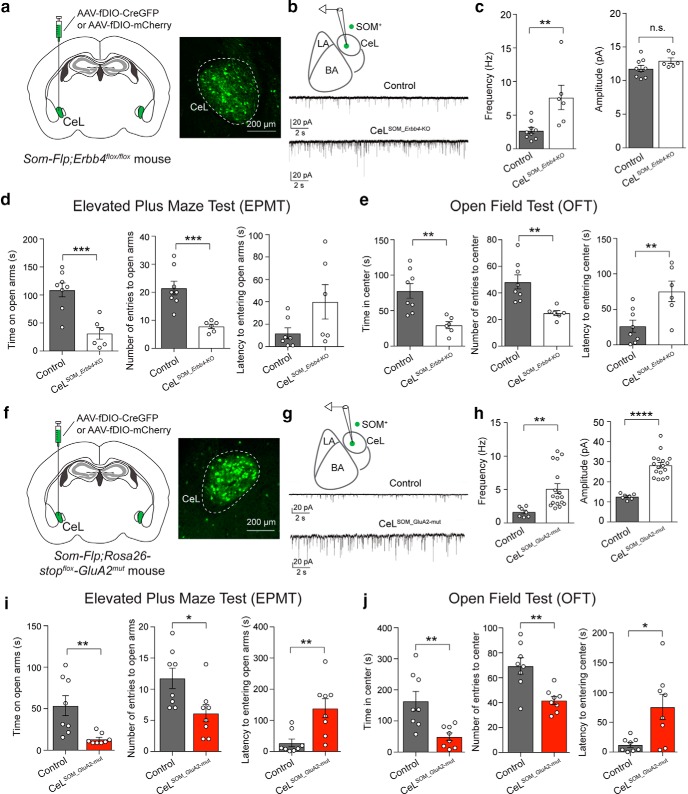
Figure 3.
Potentiation of excitatory synaptic drive onto SOM+ CeL neurons is sufficient to cause enhanced anxiety. a–e, Selective deletion of Erbb4 in SOM+ CeL neurons potentiated excitatory synapses onto these neurons and caused increased anxiety in mice. a, Left, A schematic of the experimental design. Right, An example image of the SOM+ CeL neurons expressing Cre-GFP. b, Top, A schematic of the recording configuration. Bottom, Representative mEPSC traces recorded from SOM+ neurons in the CeL of control mice (top) and mice in which Erbb4 was selectively deleted in SOM+ CeL neurons (bottom). c, Left, Quantification of mEPSC frequency. Right, Quantification of mEPSC amplitude. d, Quantification of behavioral parameters in the EPMT. e, Quantification of behavioral parameters in the OFT. f–j, Selective potentiation of excitatory synaptic transmission onto SOM+ CeL neurons was sufficient to drive enhanced anxiety in mice. f, Left, A schematic of the experimental design. Right, An example image of the SOM+ CeL neurons expressing Cre-GFP. g, Top, A schematic of the recording configuration. Bottom, Representative mEPSC traces recorded from SOM+ neurons in the CeL of control mice (top) and mice in which the GluA2mut was selectively expressed in SOM+ CeL neurons (bottom). h, Left, Quantification of mEPSC frequency. Right, Quantification of mEPSC amplitude. i, Quantification of behavioral parameters in the EPMT. j, Quantification of behavioral parameters in the OFT. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, n.s. (not significant).