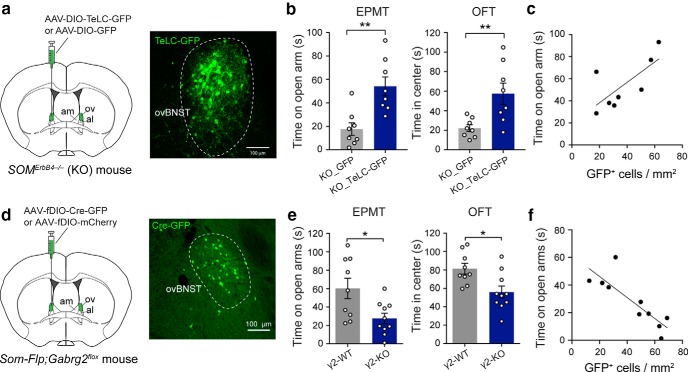
Figure 7.
The activity of SOM+ dBNST neurons is required for the enhanced anxiety in the ErbB4 mutant mice and is sufficient to drive anxiety in ErbB4 wild-type mice. a–f, For all these manipulations, we aimed at targeting the ov. However, due to the fact that the ovBNST is small and very close to the adjacent nuclei, our manipulations may have also affected other BNST nuclei, in particular the am and al areas. a, Left, A schematic of the experimental design. Right, An example image showing SOM+ ovBNST neurons expressing TeLC-GFP. b, Left, Quantification of time spent on the open are in the EPMT. Right, Quantification of time spent in the center in the OFT. c, The density of SOM+ ovBNST neurons infected with the TeLC-GFP virus correlated with the decrease in anxiety measured by the time spend on open arms during the EPMT. d, Left, Schematics of the experimental design. Right, An example image of the ovBNST in a Som-Flp;Gabrg2flox mouse, showing the expression of Cre-GFP in SOM+ ovBNST neurons. e, Quantification of measures of anxiety in the EPMT (left) and OFT (right) in the γ2-KO and γ2-WT mice. Ablation of γ2 increases anxiety. f, The density of SOM+ ovBNST neurons infected with the AAV-fDIO-Cre-GFP virus correlated with the increase in anxiety measured by the time spend on open arms during the EPMT. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM in b and e. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.