Figure 9.
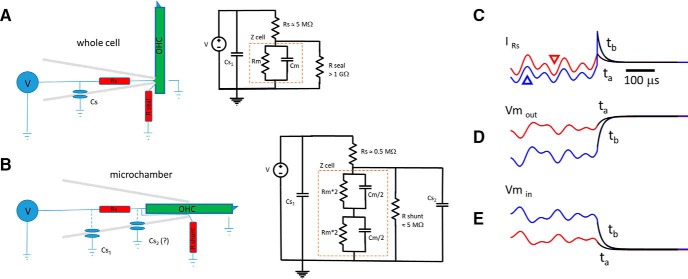
Electrical configuration of whole-cell and microchamber voltage clamp. A, Whole-cell clamp speed is limited by τ ≈ Rs * Cm. Stray capacitance (amplifier, pipette holder, and pipette) is typically modeled in a position that does not interfere with voltage-clamp speed, but can influence measured high-frequency currents if not compensated. B, The microchamber partitions the cell partway within the orifice of the macropipette. Stray Cs1 is as with whole-cell mode. The frequency response of voltage clamp also depends on Rs and Cm, since stray Cs2, if it contributes at all, is dominated by Cm. The configuration in the figure is for a cell midway in the microchamber, membrane Cm equally divided. At high frequencies, the input capacitance will be the series combination of Cm/2 and Cm/2, giving a value of Cm/4. Thus, τ ≈ Rs * Cm/4 provides a faster clamp than whole cell, but the configuration suffers from lack of DC voltage-clamp control across the membranes. With partitioning of the cell more or less within the chamber, the series combination of the nonequal partitioned cell Cm will provide an input Cm less than the smaller of the two partitioned capacitances, regardless of its location inside or outside the microchamber. Thus, clamp τ for both inserted and extruded membranes will have the same U-shaped speed function, being slowest at the half-inserted condition, as depicted. C, Displayed are two current traces (ta and tb) generated by a Matlab Simscape microchamber model using a voltage protocol similar to our DC off-set AC voltage protocol (Fig. 10B, inset). The red trace (also marked with a downward red triangle) is at zero offset, and the blue trace (also marked with an upward blue triangle) is at an offset of −65 mV. Black lines are single exponential fits. Under voltage clamp, the time course of capacitive currents mirrors the time course of the voltage delivered to the cell membrane, as shown in D and E. See text for more details.