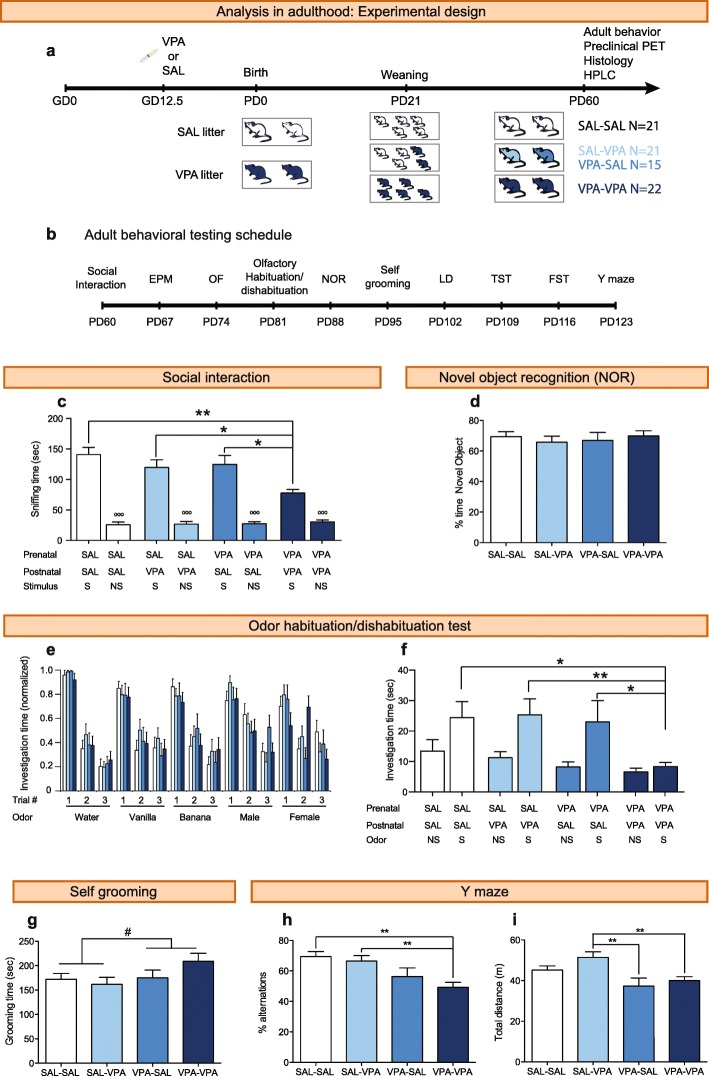
Fig. 2.
Peers can rescue the reduction in sociability observed in mice prenatally exposed to VPA, but not the increase in repetitive patterns of behavior. a Experimental design. Pregnant dams were injected with 600 mg/kg VPA or saline on gestational day 12.5. Offspring exposed to VPA (dark blue mice on PD21) and SAL (white mice on PD21) were weaned on PD21 in three type of cages. Due to interaction in the home cage until PD60, four experimental groups were generated: VPA animals weaned with other VPA animals (VPA-VPA group; dark blue); VPA animals weaned with saline mice (VPA-SAL group; blue); saline animals weaned with VPA animals (SAL-VPA group; light blue); and saline animals weaned with other saline animals (SAL-SAL group; white). b Adult behavioral analysis. Starting at PD60, all animals were subjected to a battery of behavioral tests performed in the order depicted. Tests were separated by 1-week intervals to reduce any inter-test effect. EPM, elevated plus maze; FST, forced swimming test; LD, light-dark box; NOR, novel object recognition; OF, open field; TST, tail suspension test. c Time spent sniffing the social (S) or non-social (NS) stimulus in the social interaction test. d Percentage of time exploring a novel object in the NOR test. e, f Odor habituation/dishabituation test: (E) Normalized time spent investigating each odor presentation, during three consecutive trials; (F) Time spent investigating the first presentation of non-social (NS) or social (S) odors. g Self-grooming test. h Spontaneous alternations in the Y maze. i Total distance traveled in the Y maze. Paired Student’s t test, °°°p < 0.001. Two-way ANOVA prenatal factor effect, #p < 0.05. Tukey’s post hoc test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Graphs indicate means + s.e.m. Detailed statistical information is available in Additional file 1: Table S1