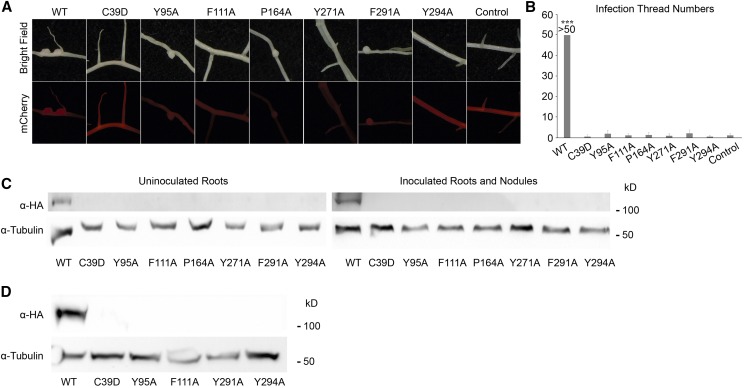
Figure 3.
MLD is required for DMI2 protein to function properly in the early nodule development process and to stabilize full-length DMI2 proteins in plants. A, Images showing representative nodules in dmi2-1 plants transforming wild-type (WT) gDMI2-HAST and MLD point mutation versions of gDMI2-HAST. Although some point mutation versions could generate nodules, most of them were white and small. mCherry fluorescence was used to select the transformed roots. B, dmi2-1 plants expressing gDMI2-HAST containing point mutations in MLD had few infection threads in a quantitative assay. The number of infection threads in dmi2-1 plants expressing wild-type gDMI2-HAST was estimated to be more than 50. More than 10 transformed plants were used for each line. Data represent means and sd. Asterisks show a significant difference (***, P < 0.001, Student’s t test). C, DMI2 protein containing amino acid substitutions in MLD is unstable in Medicago plants, with or without rhizobia inoculation. In dmi2-1 gDMI2-HAST plants, DMI2-HAST protein could be seen, while the MLD amino acid substitution version proteins were totally undetectable. D, MG132 treatment could not rescue the constitutive degradation of DMI2 protein containing amino acid substitutions. dmi2-1 plants expressing wild-type gDMI2-HAST and MLD point mutation versions were treated with 100 μm MG132, and the protein level was tested. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results.