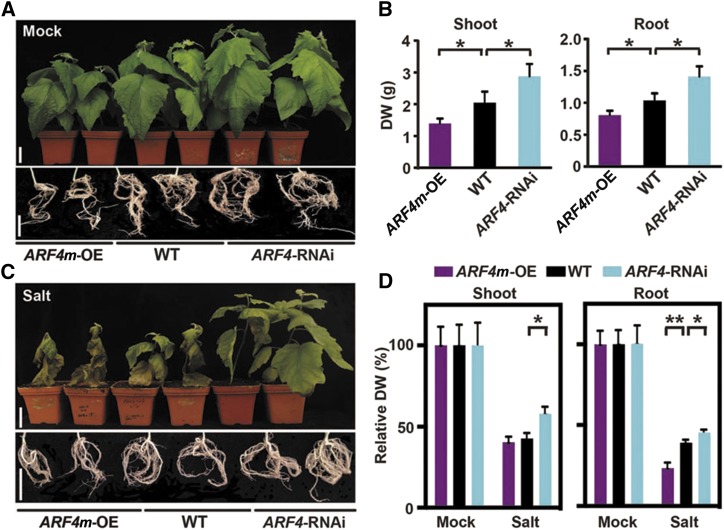
Figure 5.
ARF4 negatively regulates plant growth and salt tolerance in poplar. A, Shoot and root phenotypes of wild-type (WT), ARF4m-OE, and ARF4-RNAi plants cultivated in soil for 10 weeks. Bars = 5 cm. B, Quantitative measurements of shoot and root biomass (dry weight [DW]) of wild-type, ARF4m-OE, and ARF4-RNAi plants cultivated in soil for 10 weeks. Error bars represent sd. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test for pairwise comparisons between wild-type and transgenic lines (*, P < 0.05; n = 5). C, Shoot and root phenotypes of wild-type, ARF4m-OE, and ARF4-RNAi plants under salt treatment. Poplar plants were cultivated in soil for 4 weeks and subsequently watered with 200 mm NaCl for 6 weeks. Bars = 5 cm. D, Relative quantification of shoot (E) and root (F) biomass (dry weight) of wild-type, ARF4m-OE, and ARF4-RNAi plants under salt treatment. Poplar plants were cultivated and salinity treated as described in C. The values for each genotype under mock treatment were normalized to 100%. Nonnormalized values are given in Supplemental Figure S10, C and D. Error bars represent sd. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test for pairwise comparisons between wild-type and transgenic lines (*, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01; n = 5).