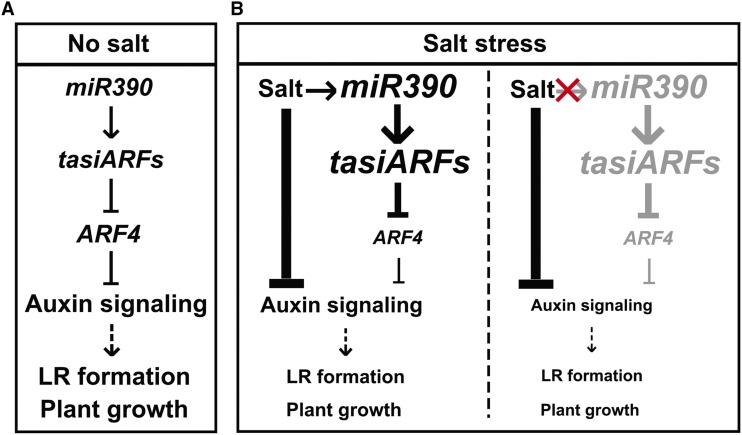
Figure 8.
Proposed model for miR390/ARF4-dependent poplar LR growth under normal and salt conditions. A, miR390 produces TAS3-derived tasiARFs that target ARF4 transcripts via direct binding. The repression of ARF4 releases auxin signaling for LR initiation and elongation. B, Left, Salt remarkably inhibits auxin signaling and induces miR390 expression. The salt-induced expression of miR390 stimulates the production of tasiARFs for the degradation of ARF4 transcripts. Attenuated expression of ARF4 facilitates the maintenance of auxin signaling against salt inhibition. Right, If the salt induction of miR390 does not occur, auxin signaling and LR formation are more seriously inhibited by salt. The miR390/tasiARF/ARF4 module is thereby essential for sustaining LR formation under salinity and salt-tolerant plant growth. Arrows represent a positive regulatory action of one component on another. Lines ending with a trait represents a negative regulatory action. The font size of words and the thickness of arrows/lines in B indicate positive (larger/thicker) or negative (smaller/thinner) regulation compared with that under the normal condition (no salt). The red cross and gray words (right) indicate the hypothetical absence of salt induction of the miR390/tasiARFs/ARF4 module.