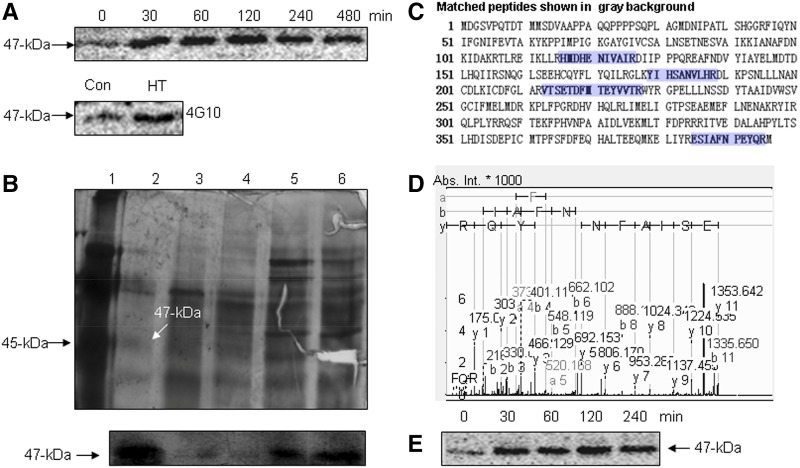
Figure 1.
Identification of HT-activated SlMPK1. A, HT-activated MBP kinase. The time courses of the induction of MBP kinase activities by HT (top) and the Tyr phosphorylation of HT-activated MBP kinase (bottom) are shown. B, Analysis of purification pools by gel electrophoresis (top) and in-gel kinase assay (bottom). Lane 1, Marker standards; lane 2, pooled fractions from the poly-l-Lys-agarose column; lane 3, pooled fractions from the Mono QTM 5/50 GL column; lane 4, pooled fractions from the Q-Sepharose HP column; lane 5, pooled fractions from the Phenyl-Sepharose FF column; lane 6, pooled fractions from the Q-Sepharose FF column. Proteins from different stages of purification were resolved on a 12% polyacrylamide gel containing SDS and stained with silver (top). The fractions were loaded onto a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel embedded with MBP, and an in-gel kinase assay was performed (bottom). C, Identification of SlMPK1 by MS/MS. A 47-kD band from the SDS-PAGE gel was cut, and the protein in-gel fragment was digested with trypsin followed by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS/MS analyses. Proteins were identified by Mascot database searches. Matched peptides are shown in blue. D, MS/MS spectrum of the selected peptide (m/z 1,777.7845). Database matching indicated that this is a fragment (ESIAFNPEYQR) of SlMPK1. Abs. Int., Absolute intensity of the y axis. E, Immunoprecipitation kinase analysis of HT-induced SlMPK1. Total proteins were extracted from the HT-treated leaves at the indicated times, and SlMPK1 activity was measured.