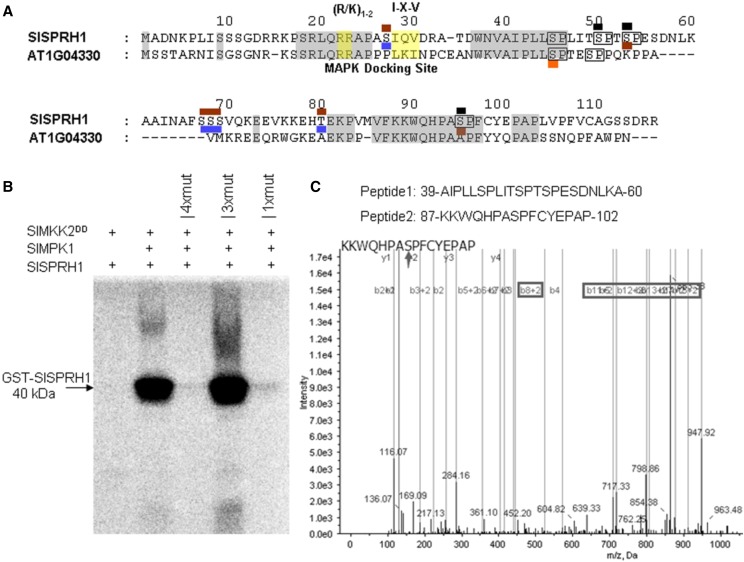
Figure 6.
Phosphorylation of SlSPRH1 by SlMPK1. A, Identification of phosphorylation sites of SlMPK1-targeted SlSPRH1 using liquid chromatography (LC)-MS/MS analysis. The amino acid sequence of SlSPRH1 and Arabidopsis homologous At1g04330 phosphorylation sites are marked. The potential MAPK target sites (S/T-P) are boxed in the SlSPRH1 sequence, where S/T-P sites detected as being phosphorylated are marked in brown in the SlMPK1-treated SlSPRH1 protein and blue in the background SlSPRH1 protein and those detected as being phosphorylated by AtMPK6 are shown in orange (Palm-Forster et al., 2012). Partial MS/MS spectra are shown in Supplemental Figure S7. B, In vitro phosphorylation of purified wild-type and mutant SlSPRH1 substrate by SlMPK1. His-tagged SlMPK1 (His-SlMPK1) and GST-tagged SlSPRH1 (GST-SlSPRH1) were used in phosphorylation reactions with 32P labeling. 4xmut indicates all identified Ser residues, Ser-44, Ser-49, Ser-52, and Ser-94, changed to Ala, 3xmut indicates all Ser residues changed to Ala except Ser-44, and 1xmut indicates only Ser-44 changed to Ala. The constitutive-active form of SlMKK2DD was used to activate SlMPK1 and as a negative control for unspecific phosphorylation of SlSPRH1 protein. Phosphorylated SlSPRH1 was visualized by a Typhoon phosphor imager after gel electrophoresis. The experiment was repeated at least three times with similar results. C, MS analysis of synthetic peptides phosphorylated in vitro by SlMPK1. Synthetic peptides were incubated with His-SlMPK1 and GST-SlMKK2DD in a kinase reaction, which was then centrifugally filtered through a Millipore 5-kD cutoff filter. The filtrate was determined by LC-MS/MS. The arrow indicates the phosphorylation site of the peptide. The phosphorylated sites are marked in black in A.