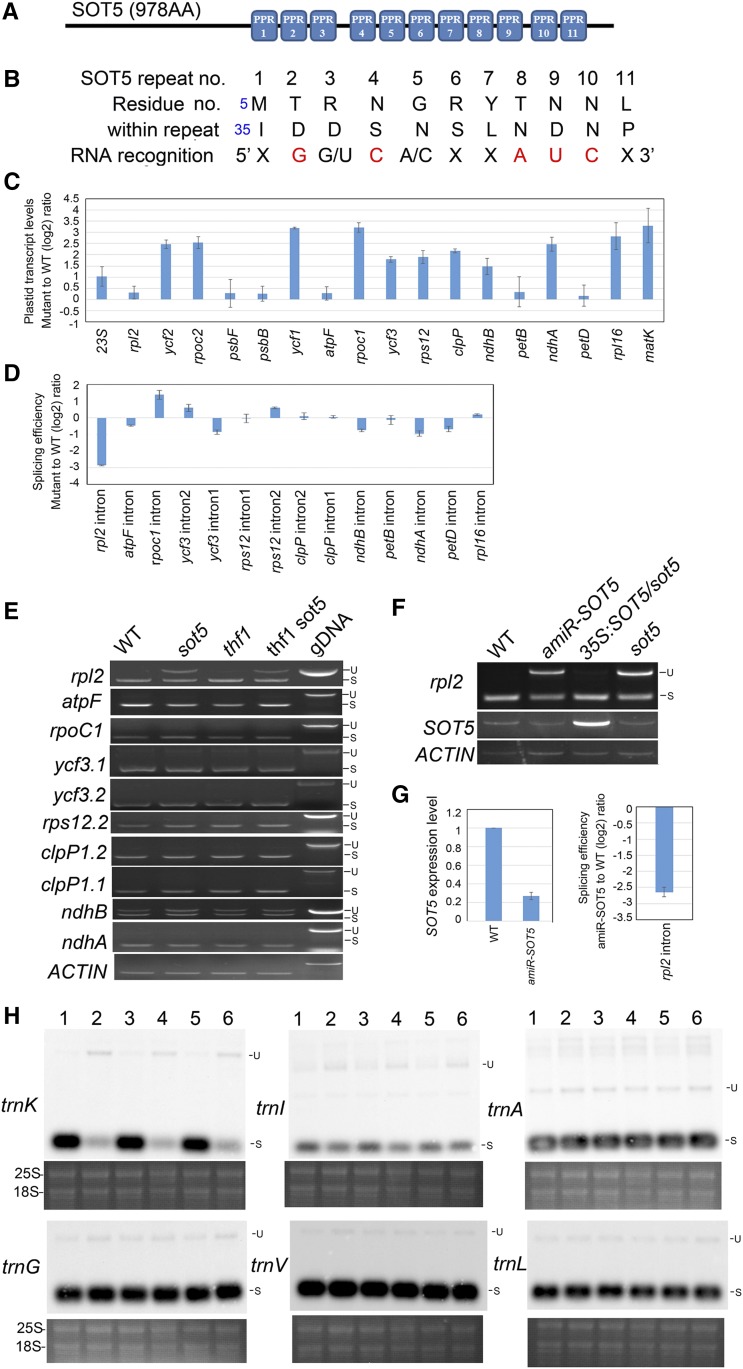
Figure 6.
SOT5 is required for the splicing of the plastid rpl2 and trnK introns. A, Schematic SOT5 protein containing 11 PPR motifs. B, Predicted 11 ribonucleotides targeted by the 11 PPR motifs shown in A. In each repeat, the two key amino acid residues and their nucleotide targets are shown. X indicates unpredictable; two nucleotides with a slash mean optional; the red nucleotides are precisely predicted. C, RT-qPCR analysis of relative expression levels of the plastid genes containing the predicted target sequences or group IIA introns in sot5. Three biological replicates were analyzed. D, Splicing efficiency analysis of 14 plastid introns in sot5 by RT-qPCR. Three biological replicates were analyzed. E, RT-PCR analysis of intron retention in eight plastid genes. Genomic DNA (gDNA) was used as a template control. S, Spliced; U, unspliced. F, RT-PCR analysis of rpl2 intron splicing in wild-type (WT), amiR-SOT5/sot5, 35S:SOT5/sot5, and sot5 plants. G, Analysis of SOT5 transcript levels and splicing efficiency of rpl2 in wild-type and amiR-SOT5 plants by RT-qPCR. H, Northern-blot analysis of plastid trn genes that contain introns in different genotypes. Lanes 1 to 6 indicate the wild type, sot5, thf1, thf1 sot5, 35S:SOT5/sot5, and amiR-SOT5, respectively. The ethidium bromide-stained gel under each blot is shown as a loading control. Two biological replicates were analyzed, and one representative result is shown.