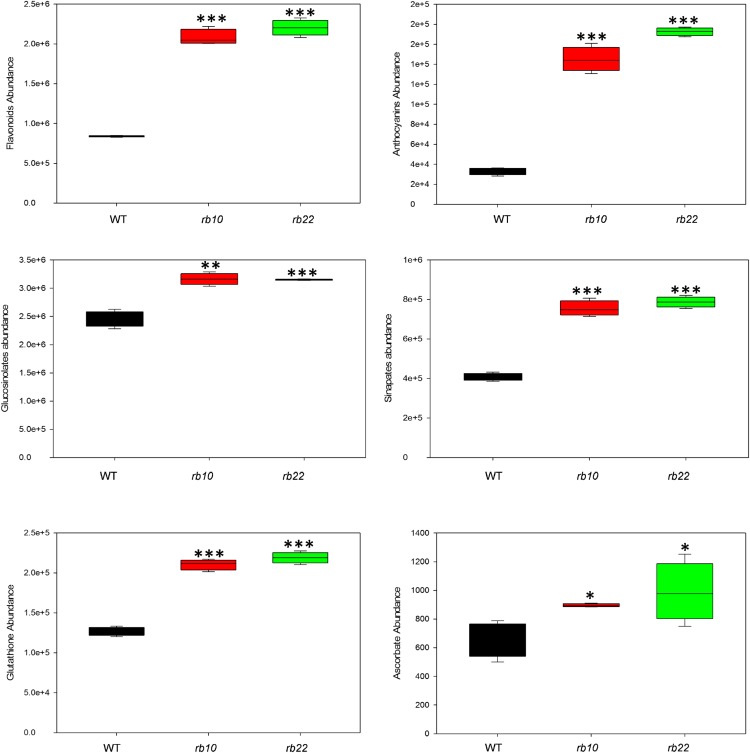
Figure 10.
Influence of raptor1b mutation on secondary metabolism. The sum of the peak intensities of detected flavonoids, anthocyanins, glucosinolates, and sinapates, as well as the intensities of glutathione and ascorbate, are shown. For extraction, the rosettes of raptor1b and the wild type (WT) were harvested from plants at the same developmental stage (10 rosette leaves). Plants were cultivated on soil under normal-light LD growth conditions. Data represent means ± sd for five biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the wild type and raptor1b under the same condition (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001, Student’s t test).