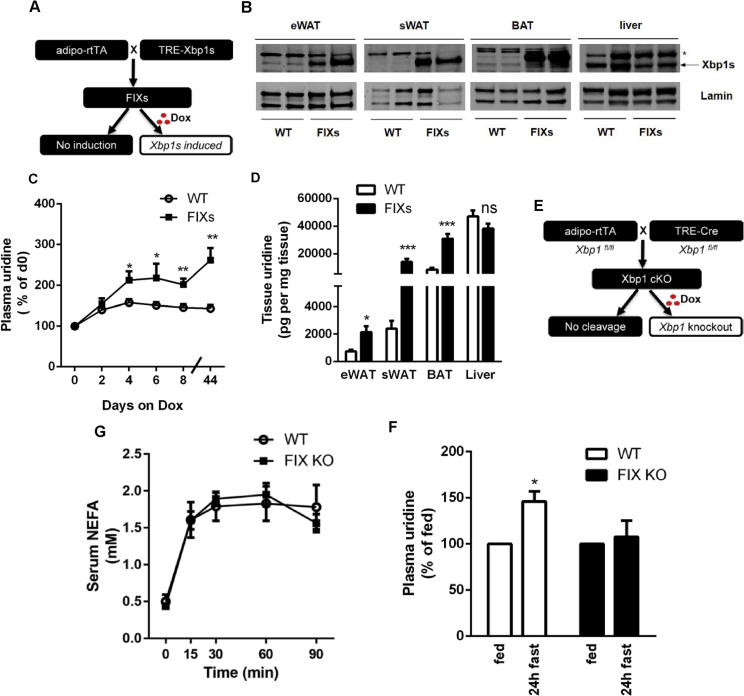
Figure 2.
Adipocyte Xbp1s is sufficient and necessary for plasma uridine elevation triggered by lipolysis. (A) Strategy for the generation of mouse with adipocyte-specific fat tissue inducible Xbp1s overexpression (FIXs). (B) Verification of Xbp1s expression by western blotting after 7 days of Dox chow feeding. Lamin was used as a loading control. * denotes a non-specific cross-reacting band. (C) Adipocyte Xbp1s overexpression increased plasma uridine levels (n = 5–6). Plasma uridine concentration from each mouse was normalized to basal level prior to Dox. Statistical analysis was performed for the two genotypes at time points indicated. (D) Adipocyte Xbp1s overexpression increased uridine concentration in fat depots (n = 6). (E) Strategy for the generation of mouse with adipocyte-specific fat tissue inducible Xbp1 knockout (FIX KO). (F) Adipocyte Xbp1 deficiency prevented plasma uridine elevation in fasted mice (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed for each genotype using the fed state of that group as base line. (G) Serum NEFA was increased by CL316, 243 in both WT and FIX KO mice (n = 3). Data in (C), (D), and (G) were analyzed with two-tailed Student t test, and data in (F) was analyzed with paired t test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001. Error bars denote SEM.