Fig. 5.
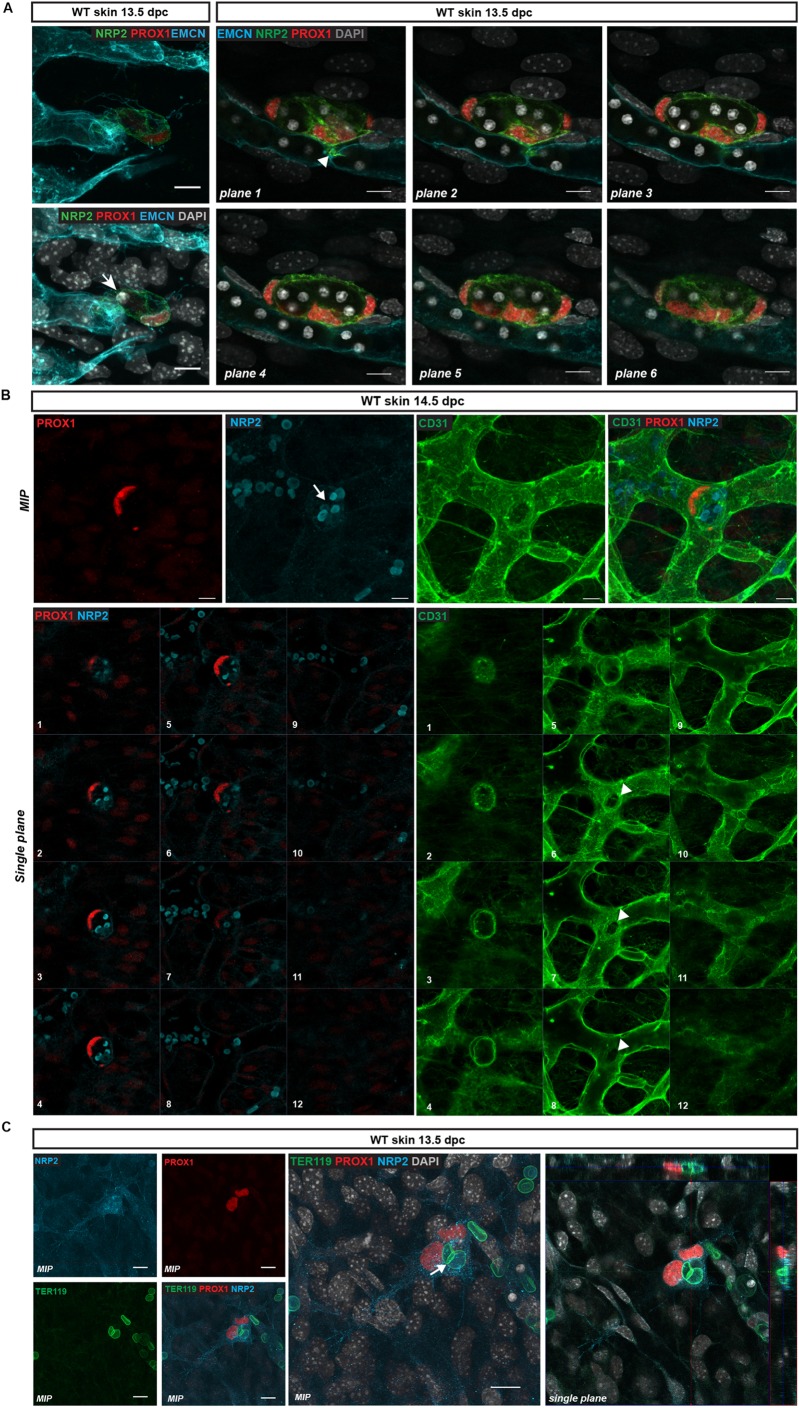
LEC clusters bud from the dermal blood vascular capillary plexus. (A) Left: Whole-mount immunostaining of wild-type (WT) embryonic skin at 13.5 dpc. LEC progenitors stained with NRP2 (green) and PROX1 (red) delaminate from the endomucin-positive capillary plexus (blue). Staining of the nuclei with DAPI reveals that this event is associated with the encapsulation of red blood cells (arrow). Right: Whole-mount immunostaining of WT embryonic skin at 13.5 dpc for EMCN (blue), NRP2 (green) and PROX1 (red) showing multiple PROX1-positive LEC progenitors undergoing cell extrusion from the capillary plexus. Each image corresponds to a single plane through a maximum intensity projection (MIP). Arrowhead indicates the connection point between the LEC cluster and the blood vascular plexus. Red blood cells, visualised by DAPI staining, are encapsulated by LECs. (B) Whole-mount immunostaining of WT embryonic skin at 14.5 dpc for PROX1 (red), CD31 (green) and NRP2 (blue) showing a PROX1-positive lymphatic cluster emerging from the blood vascular plexus, encapsulating multiple red blood cells (arrow; highlighted by NRP2). Top panels show MIPs, bottom panels show individual single planes (1-12) through the MIP showing the connection between the lymphatic cluster and blood vascular plexus (arrowheads). Plane 1 depicts the top of the cluster, and planes 6-8 show the connection point with the blood vasculature. (C) Whole-mount immunostaining of WT embryonic skin at 13.5 dpc. LEC cluster stained with NRP2 (blue) and PROX1 (red) showing encapsulation of red blood cells (stained with TER119 antibody, green). Arrow indicates red blood cell present within the LEC cluster. Left panels show MIPs, right panel shows an orthogonal projection from the z-stack with xz and yz views showing the encapsulated red blood cell. Scale bars: 10 μm.