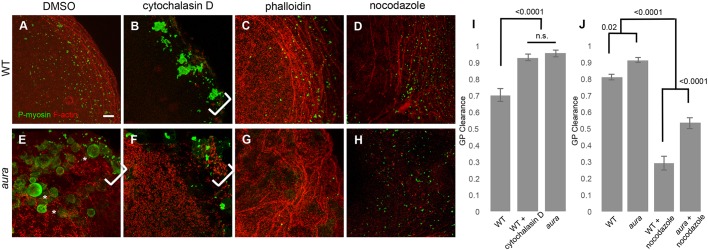
Fig. 5.
Modulation of germ plasm RNP outward movement depends on cortical F-actin. (A-H) RNPs (green) and cortical F-actin (red) in control- (DMSO), cytochalasin D-, phalloidin- and nocodazole-treated wild-type (A-D) and aura mutant (E-H) embryos. F-actin inhibition with cytochalasin D in wild-type embryos leads to large RNP aggregates at the distal edge of the blastodisc (B), mimicking the aura mutant phenotype (E; large spherical structures are retained cortical granules; Eno et al., 2016). F-actin stabilization with phalloidin (C,G) does not have a significant effect in wild type (C) but reduces ectopic RNP aggregate accumulation in aura mutants (G). Inhibition of microtubules with nocodazole (D,H) results in reduced outward RNP movement in both wild type (D; Theusch et al., 2006) and aura mutants (H). Brackets indicate ectopic marginal RNP aggregate accumulation. (I,J) Quantitation of RNP outward clearing. Significance was determined using an unpaired t-test. Data are mean±s.e.m. Scale bar: 10 μm.