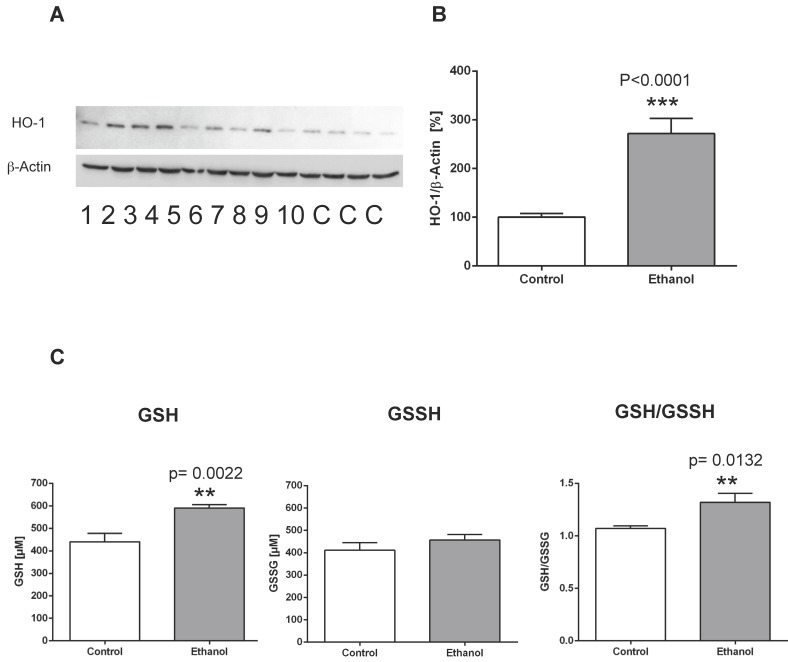
Figure 1.
Chronic alcohol consumption increases the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in the liver. (A) Representative Western blot of HO-1 in the liver of rats fed with an alcohol-containing diet for 12 weeks (ethanol, lanes 1-10) and controls (lanes C; for more clarity, protein lysates of controls have been pooled). Detection of β-actin served as loading control. This example is representative of a series of blots. (B) Quantification of bands expressed as density ratio of indicated protein/β-actin (%; control set to 100%); ***p<0.0001 compared with controls; data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=10). (C) Chronic alcohol consumption modifies levels of reduced glutathione (GSH) and oxidized glutathione (GSSG) in the liver as detected by the reaction with the thiol reagent DTNB (left/middle panel). GSH/GSSH ratio (right panel). **p<0.01 compared with controls; data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=10).