Figure 3.
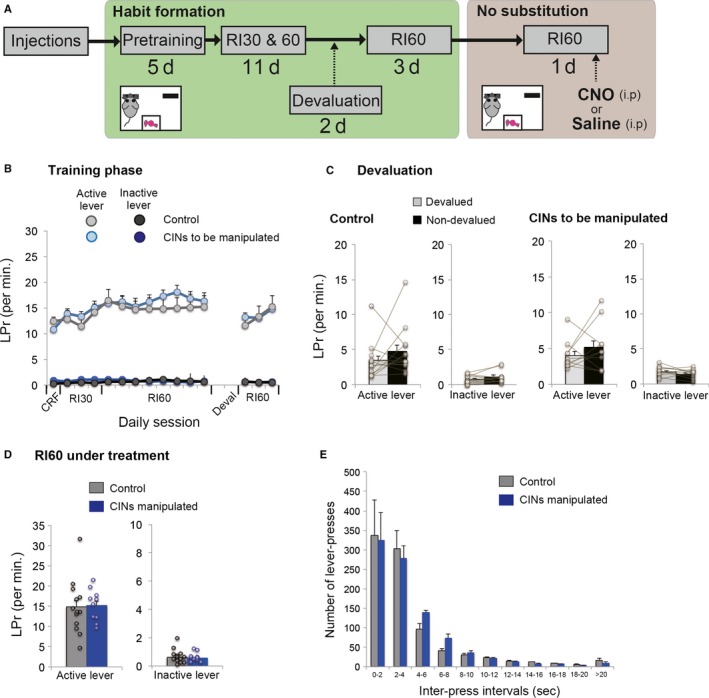
Chemogenetic activation of CINs in responses under a RI60 schedule without habit substitution. (A) A flow chart of experiment 3. Similar to the Experiment 1, animals formed a habit under the random‐interval schedule. In a test day, animals with or without CIN activation perform the same RI60 schedule without a switch of habitual responses. This procedure controls the effect of activating CINs on lever‐press behaviour and its reinforcement in general. (B) Lever‐press rate during a habit formation period under RI schedules. (C) Lever‐press rate during an outcome devaluation test. Note that both groups successfully formed a habit as confirmed by insensitivity to the outcome devaluation. (D) Lever‐press rate on both active and inactive levers in a test day under the same RI60 schedule. (E) Inter‐press intervals of habitual responses to an active side on the same testing day. Note that CIN activation had no effect on responses. Scatter plots indicate individual data points. Final group size is follows: control rats, n = 13 (virus‐control = 5; CNO‐control = 8); CINs manipulated rats, n = 10.
