Figure 4.
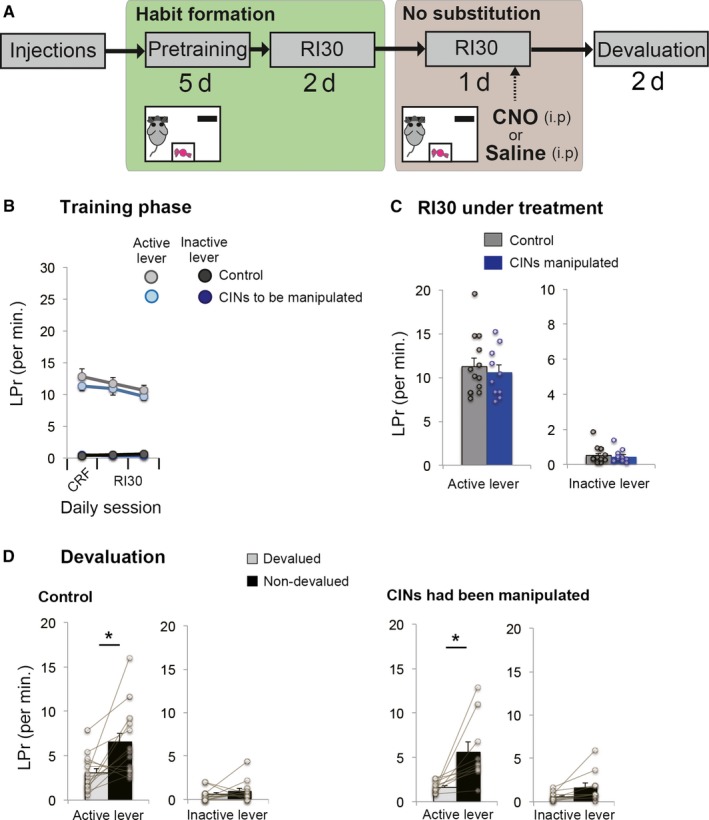
Chemogenetic activation of CINs in an early phase of learning. (A) A flow chart of experiment 4. Animals underwent a continuous reinforcement schedule followed by RI30. Unlike the other experiments, chemogenetic activation was performed 2 days after the initiation of RI30 schedule. After the one‐day activation, the devaluation test was performed to examine whether the prior treatment accelerated habit formation. This procedure controlled for the facilitative effect of activating CINs on new lever‐press learning or habit formation, regardless of switching habits. (B) Lever‐press rate before cholinergic manipulation. Experiment and control groups showed similar baseline lever‐press rates. (C) Performance of RI30 under cholinergic manipulation. Cholinergic activation does not affect lever‐press performance in the early phase of learning. (D) A devaluation test following cholinergic activation showed that both control and rats with cholinergic interneurons that had been activated are sensitive to outcome devaluation, indicating that there is no effect of the cholinergic manipulation on lever‐press rate or habit learning before the habit has been formed. Scatter plots indicate individual data points. Final group size is follows: control rats, n = 13 (virus‐control = 7; CNO‐control = 6); CINs manipulated rats, n = 10.
