Figure 8.
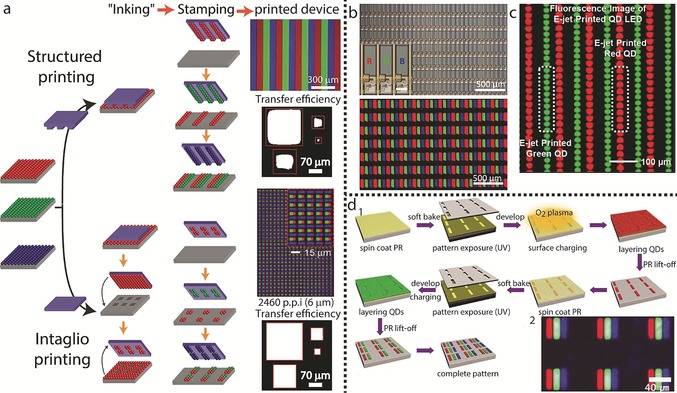
Assembly techniques for display applications. a) Two mechanisms for transfer printing are illustrated: structured printing, in which the stamp replicates its pattern to the substrate upon stamping, and intaglio printing, in which the “inked” patternless stamp is pressed onto an engraved surface, to retain its “negative” pattern, which is later transferred to the substrate. Both methods lead to full‐color CQDs patterns. The upper image above the printed device column for each printing method depicts PL images of the transfer‐printed RGB QD patterns (reprinted from Refs. 110 and 111 with permission), while the lower part shows the transfer efficiencies of a pattern with different sizes, comparing the resolution limitations of both methods (reprinted from Ref. 111 with permission). b) A full‐color QD active matrix display fabricated by ink‐jet printing. The top panel shows microscopy images of the pixel arrays. Inset: magnified image of RGB subpixels; the lower panel shows an EL image of RGB subpixel arrays. Reprinted from Ref. 115 with permission. c) A PL image of green and red QD arrays printed by e‐jet printing (reprinted from Ref. 116 with permission). d) 1. Illustration of a patterning technique involving alternating photolithography and LBL assembly steps for the patterning of R, G, and B CQDs. 2. PL image of the patterned substrate (reprinted from Ref. 117 with permission).
