Figure 2.
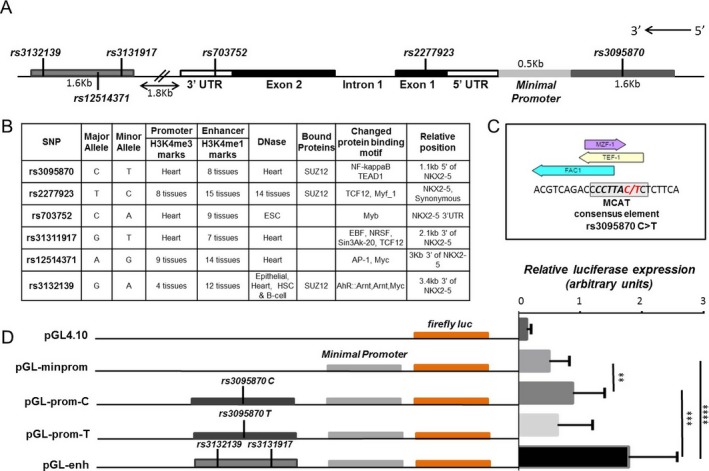
Disease‐associated single‐nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in functional regulatory regions. A, Schematic representation of the NKX2-5 gene with its introns, exons, and untranslated regions (3′‐UTR and 5′‐UTR). The location of the tagging SNPs is shown in the schematic map of the NKX2-5 genomic locus. B, Findings of in silico analysis of the tagging SNPs using HaploReg and Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) data. C, Transcription factor binding sites around rs3095870, as determined using the TRANSFAC and JASPAR databases. Boxed area shows the consensus‐binding element for transcription‐enhancer factor domain 1 (TEAD1) on the MCAT site; the alleles of rs3095870 are shown in red. D, Transcriptional activity in primary human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells transfected with reporter gene constructs containing the minimal promoter (pGL‐minprom), upstream promoter with either the rs3095870 C allele (pGL‐prom‐C) or the rs3095870 T allele (pGL‐prom‐T), or the downstream enhancer (pGL‐enh) are shown at the left. The pGL4.10 vector, which contains the firefly luciferase (luc) gene, was used as the cloning vector. The relative luciferase expression for each of the 5 constructs is shown at the right. Values are the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. ** = P < 0.01; *** = P < 0.001; **** = P < 0.0001 by Student's t‐test. TCF‐12 = T cell factor 12; ESC = embryonic stem cell; EBF = early B cell factor; NRSF = neuron‐restrictive silencer factor; AP‐1 = activator protein 1; HSC = hematopoietic stem cell; AhR = aryl hydrocarbon receptor; ARNT = aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator; MZF‐1 = myeloid zinc finger 1; TEF‐1 = transcriptional enhancer factor 1. Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.40419/abstract.
