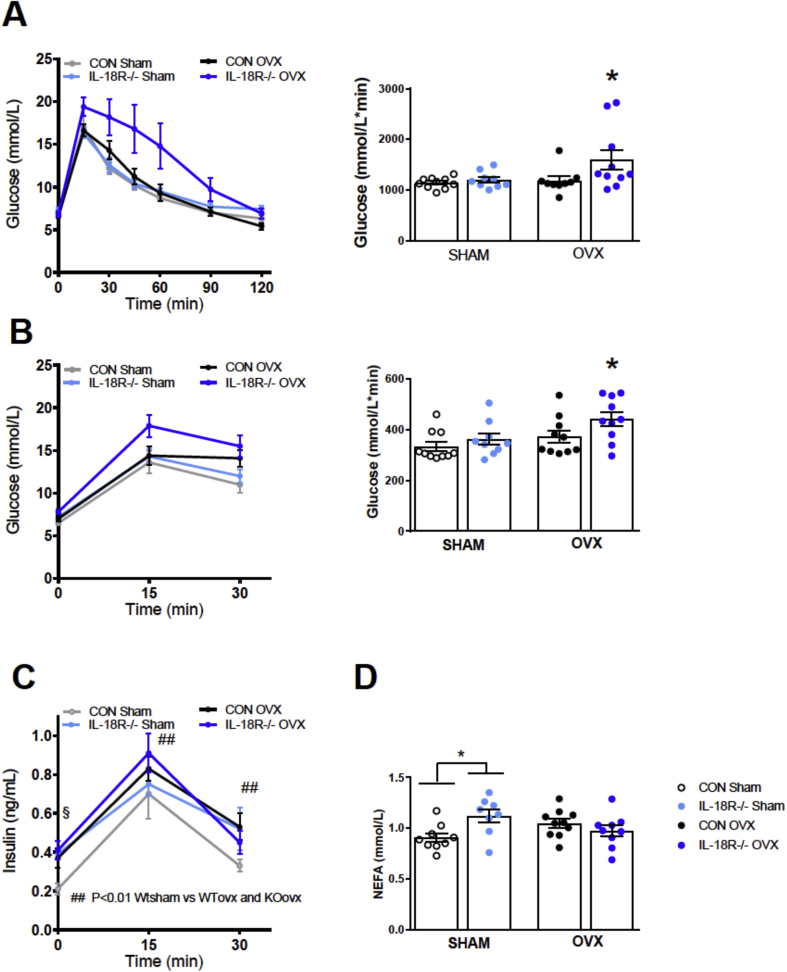
Figure 4.
Ovariectomized IL-18R−/− mice exhibit impaired glucose tolerance and insulin resistance. A: Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance with area under the curve (AUC) inserted in Sham and ovariectomized mice 16 weeks after operation (CON-Sham: n = 10; CON-OVX n = 9; IL-18R−/−-Sham: n = 9; IL-18R−/−-Ovx: n = 10). B: Oral glucose tolerance with area under the curve (AUC) inserted in Sham and Ovx animals 17 weeks after operation (CON-Sham: n = 10; CON-OVX n = 10; IL-18R−/−-Sham: n = 9; IL-18R−/−-OVX: n = 10); C: Plasma insulin during an oral glucose tolerance test in Sham and Ovx animals 17 weeks after operation (CON-Sham: n = 10; CON-OVXx n = 10; IL-18R−/−-Sham: n = 9; IL-18R−/−-OVX: n = 10); D: Fasted NEFA concentration in Sham and Ovx animals 17 weeks after operation (CON-Sham: n = 10; CON-OVX n = 10; IL-18R−/−-Sham: n = 9; IL-18R−/−-OVX: n = 10). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 vs CON Sham (A, B, D: one-way ANOVA, difference between four groups); *p < 0.05 vs CON Sham/KO Sham and CON OVX (A, B: No difference between CON Sham and KO sham and the groups were pooled to one group. One-way ANOVA between three groups); ##p < 0.01 (C: CON OVX and KO OVX vs CON Sham); §p = 0.056 versus CON OVX, CON Sham and KO sham, two-way ANOVA (4 groups (CON-sham, CON-OVX, KO-sham, KO-OVX) and Time (15 and 30 min)).