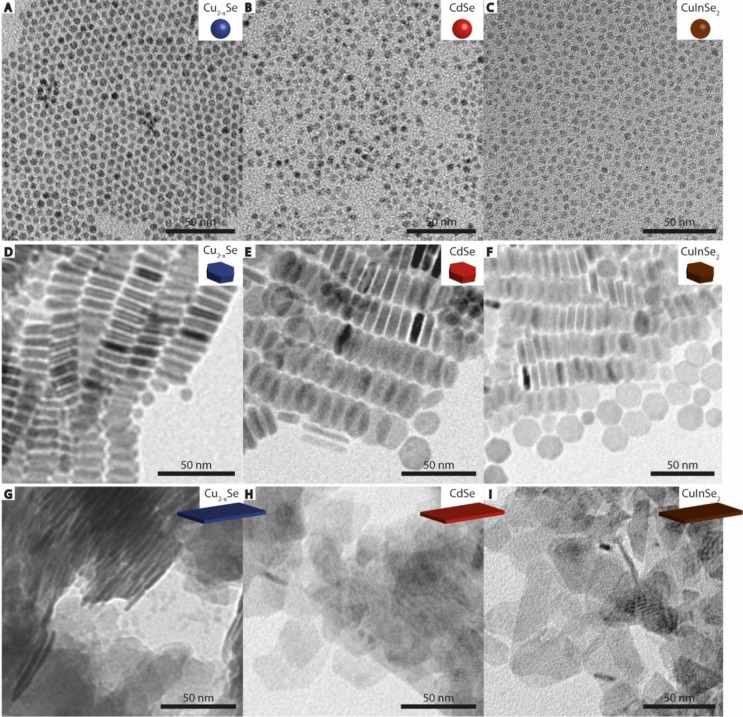
Figure 4.
TEM images of (A) template Cu2–xSe quantum dots, d = 4.9 ± 0.5 nm. (B) Product CdSe quantum dots with d = 4.1 ± 0.7 nm, obtained by Cu+ for Cd2+ cation exchange using the NCs shown in (A) as templates. (C) Product CuInSe2 quantum dots with d = 3.6 ± 0.7 nm, obtained by partial Cu+ for In3+ cation exchange using the NCs shown in (A) as templates. (D) Template Cu2–xSe nanoplatelets (h = 7.0 ± 0.5 nm, l = 17 ± 2 nm). (E) Product CdSe nanoplatelets with h = 6.0 ± 0.7 nm and l = 21 ± 3 nm, obtained by Cu+ for Cd2+ cation exchange using the NCs shown in (D) as templates. (F) Product CuInSe2 nanoplatelets (h = 4.9 ± 0.7 nm, l = 21 ± 1 nm) obtained by partial Cu+ for In3+ cation exchange using the NCs shown in (D) as templates. (G) Template ultrathin Cu2–xSe nanosheets (h = 2.4 ± 0.4 nm, l = 50–100 nm). (H) Product ultrathin CdSe nanosheets obtained by Cu+ for Cd2+ cation exchange using the NCs shown in (G) as templates. (I) Product CuInSe2 nanosheets obtained by partial Cu+ for In3+ cation exchange using the NCs shown in (G) as templates. All scale bars correspond to 50 nm.