Figure 10.
SUMOylation of SIZ1 at K100, K479, and K488 Does Not Alter SIZ1 Activity nor Its Phenotypic Functions.
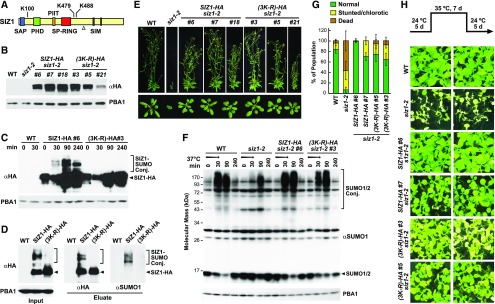
(A) Organization of the SIZ1 protein. The SAP, PHD, PIIT, SP-RING, and SIM domains are highlighted in blue, green, orange, red, and purple, respectively. Positions of the modified lysines are indicated. The open triangle marks the termination in siz1-2 protein sequence generated by the T-DNA insertion.
(B) Immunoblot detection of SIZ1 protein in wild-type and siz1-2 seedlings or in a collection of siz1-2 seedlings independently transformed with transgenes encoding HA-tagged SIZ1 or SIZ1 variant in which the lysines at positions K100, K479, and K488 were substituted for arginines [(3K-R)-HA]. The membrane was probed with either anti-HA or anti-PBA1 antibodies (loading control).
(C) Accumulation of SUMOylated forms of SIZ1 during heat stress. Seven-day-old wild-type, SIZ1-HA siz1-2, and (3K-R)-HA siz1-2 seedlings were exposed to heat stress at 37°C for 30 min; total lysates were probed for SIZ1-SUMO1/SUMO2 conjugates by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibodies using anti-PBA1 antibodies as loading control. Unmodified SIZ1-HA and possible SUMO1/SUMO2 conjugates are highlighted by the arrowheads and brackets, respectively.
(D) Detection of SUMO1/2-SIZ1 conjugates by immunoprecipitation. Seven-day-old wild-type, SIZ1-HA siz1-2, and (3K-R)-HA siz1-2 seedlings were exposed to 37°C for 30 min as in (C). SIZ1 protein was isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibodies; the eluate was then subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-HA and anti-SUMO1 antibodies. The left panel shows the levels of HA-tagged SUMO1 before enrichment (Input). Unmodified SIZ1-HA and possible SUMO1 conjugates are highlighted by the arrowheads and brackets, respectively.
(E) Representative wild type, siz1-2, and SIZ1-HA or (K3-R)-HA complemented siz1-2 plants described in (B) were grown for 40 d (top) and 20 d (bottom) in a long-day photoperiod.
(F) Heat stress-induced SUMOylation of 7-d-old wild-type, siz1-2, SIZ1-HA siz1-2, and (3K-R)-HA siz1-2 seedlings. Seedlings were exposed to 37°C for 30 min (arrow) before return to a normal growth temperature of 22°C. Total lysates were probed with either anti-SUMO1 or anti-PBA1 antibodies (loading control). Free SUMO1/SUMO2 is indicated by the arrowhead.
(G) and (H) SUMOylation of SIZ1 at K100, K479, and K488 is not essential for thermotolerance to moderately high temperatures. Diagram of the heat treatment and recovery time course is shown in (H).
(G) Quantification of seedling phenotype after the heat tolerance assay. Each bar represents the mean of four biological replicates (±sd) analyzing at least 25 seedlings each.
(H) Representative wild-type, siz1-2, SIZ1-HA, or (K3-R)-HA complemented siz1-2 seedlings subjected to the temperature treatment. The plants were photographed after the 5-d recovery. Shown are two biological replicates, each consisting of 40 seedlings.