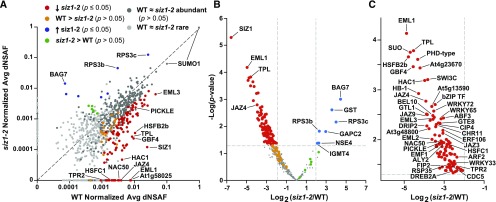
Figure 4.
Changes in the SUMO1/SUMO2 Conjugate Accumulation Patterns during Heat Stress in siz1-2 Versus Wild-Type Seedlings.
SUMO1/SUMO2 conjugates detected with at least two PSMs per biological replicate of independently grown seedlings were quantified based on their dNSAF values, which were then normalized based the dNSAF values for SUMO1.
(A) Average normalized dNSAF values of 922 SUMOylated proteins in heat-stressed siz1-2 versus wild-type seedlings (see Figure 3B). Each data point represents the average of five biological replicates of independently grown seedlings. Light-gray points are conjugates considered to be “rare” by their detection in less than three biological replicates in both backgrounds (siz1-2 and/or the wild type). Dark-gray points are conjugates considered to be “abundant” by their detection in three or more biological replicates in either background (siz1-2 and/or the wild type). Proteins with a significant decrease or increase in SUMOylation in the siz1-2 mutant compared with the wild type (P value ≤ 0.05) are highlighted in red and blue, respectively. SUMO targets identified in all wild-type biological replicates and never or only once in the siz1-2 mutant (the wild type > siz1-2), but were above the significance threshold of P value > 0.05, are in orange. Proteins detected in all siz1-2 biological replicates and never or only once in the wild type (siz1-2 > the wild type), but were above the significance threshold (P value > 0.05), are in green. The dashed line represents the theoretical situation where conjugate abundance in the wild type and siz1-2 is equal. Note that two dNSAF values are assigned to SUMO1 by Morpheus Spectral Counter.
(B) Volcano plot of the P value for individual SUMO1/SUMO2 conjugates versus the log2 fold change in wild-type versus siz1-2 seedlings. Missing values were imputed for each biological replicate. The color scheme is the same as in (A). The horizontal dashed line highlights a P value = 0.05. The vertical dashed lines highlight a 4-fold increase or decrease.
(C) Expanded view of (B) highlighting the proteins with a significant reduction of SUMOylation in the siz1-2 mutant. Notable proteins are indicated in (A) to (C).