Figure 1.
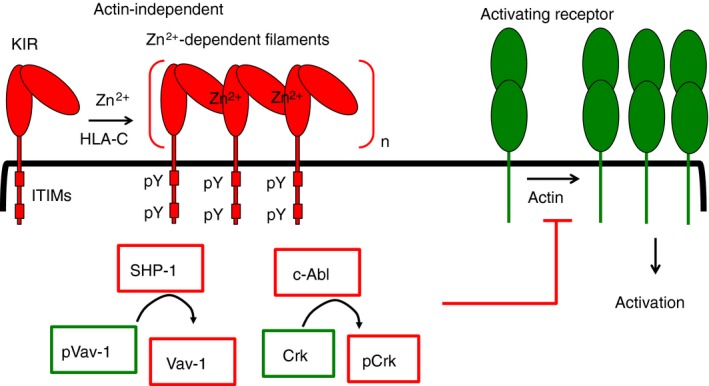
Interception of natural killer (NK) cell activation by killer‐cell Ig‐like receptor (KIR). At the inhibitory synapses formed between KIR+ NK cells and HLA‐C+ target cells, KIR clusters rapidly, in actin‐independent manner. The zinc‐dependent polymerization of KIR into filaments could contribute to the rapid and actin‐independent KIR clustering at these synapses. The Src family kinase Lck and Fyn are candidate kinases for immunoreceptor Tyr‐based inhibitory motif (ITIM) phosphorylation. The protein Tyr phosphates SHP‐1, recruited and activated by its interaction with phospho‐ITIMs (pITIMs), dephosphorylates the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav‐1. The c‐Abl kinase is recruited to the inhibitory synapses through an unknown mechanism. The c‐Abl kinase phosphorylates the small adaptor protein Crk, and dissociates it from a signalling complex (not shown here) formed during activation. Vav‐1 dephosphorylation and Crk phosphorylation contribute to blockage of actin‐dependent signals for NK cell activation, and thus could contribute to inhibition of proximal actin‐dependent steps, such as LFA‐1 activation (not shown here) and clustering of activating receptors.
