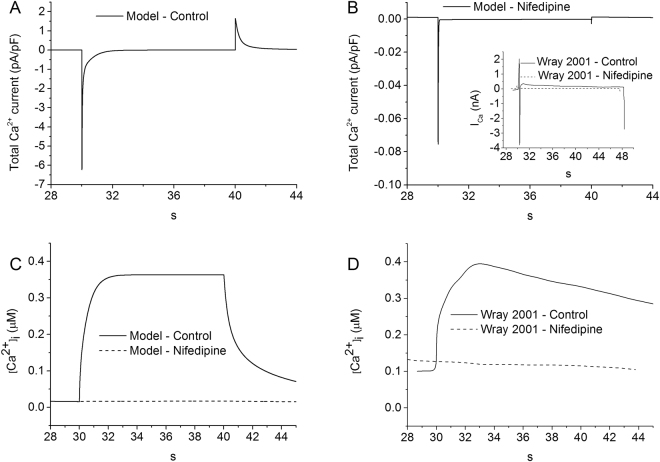
Figure 7.
The influence of 10 µM of nifedipine on the total calcium current and Ca2+ transients. A voltage clamp from −80 to 0 mV was applied to the cell membrane for 10 seconds. (A,B) The membrane voltage response to the control and nifedipine conditions respectively, showing a drop of approximately 100 times in the maximum current value. B (inset): Experimental data from Wray et al. demonstrating the drop in current due to the action of nifedipine42. Both simulations (C) and experiments (Wray et al.42) (D) suggest that in the presence of nifedipine, applying a voltage across the membrane prevents an influx of calcium into the cell.