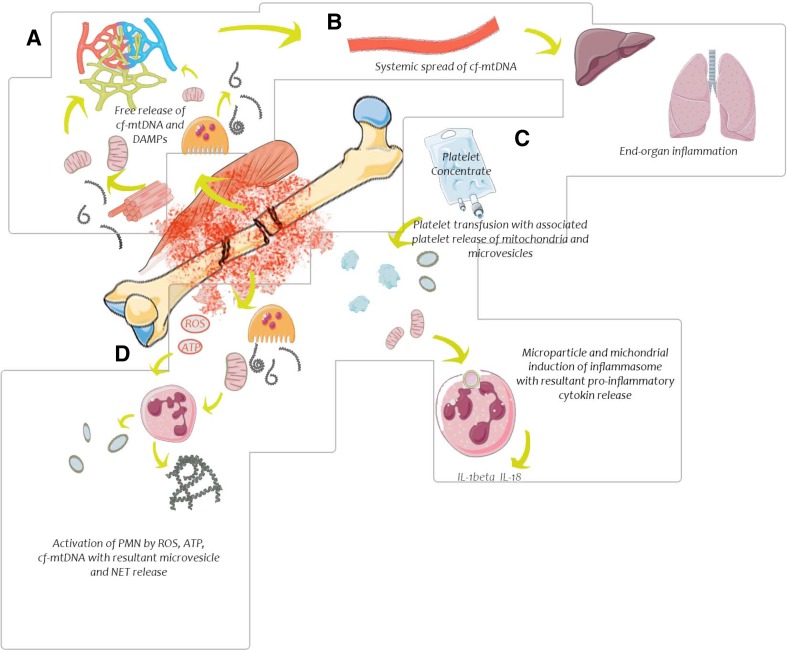
Fig. 1.
Cell-free mitochondrial DNA in trauma. This figure shows the cellular response to tissue injury. a In the immediate area of injury, cf-mtDNA is release from injured cells. b Transport of cf-mtDNA occurs through circulation to remote areas resulting in end-organ injury. c Platelet concentrate infusions contain activated platelets with cf-mtDNA and increase the cf-mtDNA load. d Generation of ATP, ROS in combination with release of mitochondrial DAMPs activate immune cells and platelets to release inflammatory cytokines