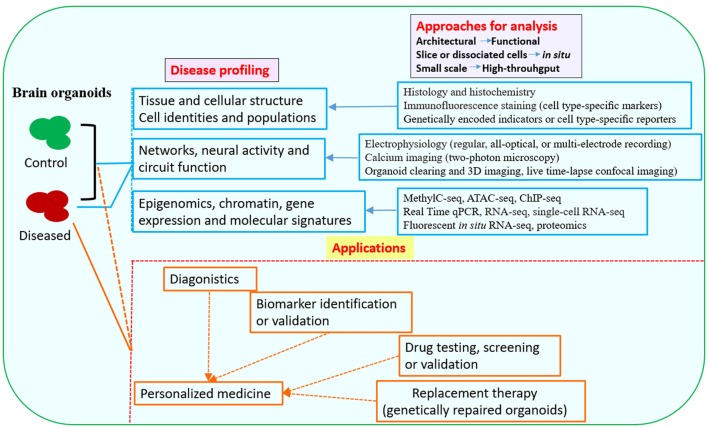
Figure 2.
Downstream analysis and applications of human brain organoid models of neurological diseases. Conventional methods used in neurobiology might not be able to exploit the neuronal activity and network connectivity within the 3D architecture of brain organoids. The combination of advanced multi-level and high-throughput detection techniques which allow analysis of the whole or intact brain organoids, will greatly benefit phenotypic profiling of human brain organoid models and may help to further uncover mechanisms for disease pathogenesis (Mariani et al., 2015; Luo et al., 2016; Qian et al., 2016; Quadrato et al., 2016; Bershteyn et al., 2017; Hartley and Brennand, 2017; Renner et al., 2017; Xiang et al., 2017; Paşca, 2018). The brain organoid models could be potentially used in drug testing or screening, identification of new biomarkers or development of innovative diagnostics and therapeutics. Patient-derived brain organoids, together with drug testing, diagnostic or therapeutic approaches, might eventually lead to personalized medicine for the individuals (Kelava and Lancaster, 2016a; Qian et al., 2016; Quadrato et al., 2016; Di Lullo and Kriegstein, 2017; Quadrato and Arlotta, 2017). Abbreviations: ATAC-seq, assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing; ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation and sequencing; MethylC-seq, MethylC-sequencing; qPCR, quantitative PCR; RNA-seq, RNA-sequencing.