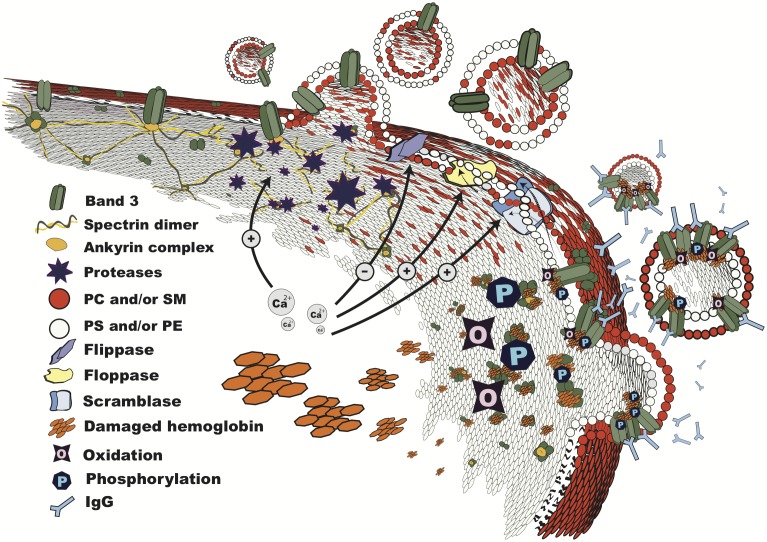
FIGURE 1.
Vesiculation in progress. Structure of the RBC membrane during vesiculation, showing mechanisms involved in microvesicle shedding: breakdown of the cytoskeleton by calcium-dependent proteases; lipid bilayer rearrangement due to altered phospholipid transporter activities, which results in phosphatidylserine exposure; changes in band 3 configuration and distribution due to oxidation, binding of damaged hemoglobin, and phosphorylation, leading to loss of binding to the cytoskeleton at the ankyrin complex, recognition by IgG, and vesiculation. The order and interdependence of these processes are discussed in the text. PC, phosphatidylcholine; SM, sphingomyelin; PS, phosphatidylserine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine.