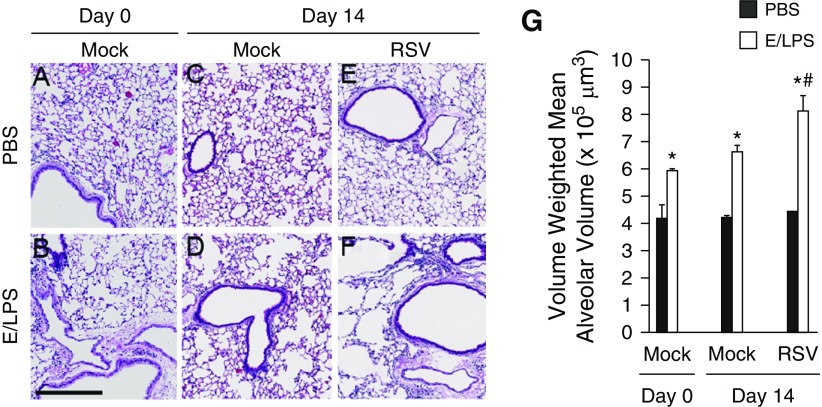
Figure 7.
RSV infection worsens emphysematous changes in E/LPS–injured mice. Lungs of (A) PBS + Mock and (B) E/LPS + Mock at Day 0, and (C) PBS + Mock–, (D) E/LPS + Mock–, (E) PBS + RSV–, and (F) E/LPS + RSV–treated mice at Day 14 were inflated to a constant pressure, paraffin embedded, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Lungs from the PBS + Mock or PBS + RSV group (Day 14 postinfection) showed normal alveolar morphology. In contrast, lungs from E/LPS + Mock or E/LPS + RSV groups (Day 14 postinfection) had mild to moderate emphysema. Images are representative of lungs from eight different mice per group. (G) The volume-weighted mean alveolar volume was calculated from measurements made on at least 25 random fields per slide. Lungs from E/LPS + Mock–treated mice had increased volume-weighted mean alveolar volume compared with PBS + Mock–treated mice. RSV infection of the E/LPS-treated mice increased volume-weighted mean alveolar volume when compared with E/LPS + PBS–treated mice; n = 8 mice per group; data reported as mean (±SD); *P < 0.05, different from PBS group; #P < 0.05, different from E/LPS + PBS group; scale bar: 250 μm.