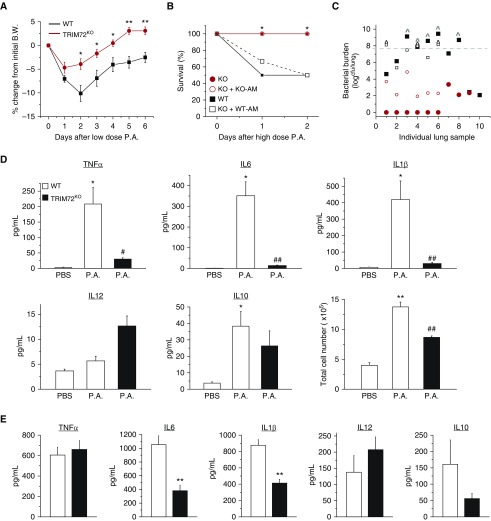
Figure 6.
TRIM72 ablation improves bacterial clearance and survival in P.a. pneumonia. (A) Percent body weight (B.W.) loss of naive WT and TRIM72KO mice after the first intraperitoneal injection of roughly 2.5 × 105 cfu/ml PAO1 (a clinical isolate of P.a.); n = 13 for WT (black squares), n = 8 for TRIM72KO (red circles), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005 compared with WT. (B) Percentage of survival at Day 2 after roughly 3 × 107 cfu/ml P.a. intraperitoneal injection; n = 10 for WT (solid black squares) and TRIM72KO (solid red circles), n = 6 for adoptive transfer of WT AM to TRIM72KO (open black squares) and for KO AM to TRIM72KO (open red circles); *P < 0.05 for WT versus TRIM72KO groups, and for WT AM to TRIM72KO versus KO AM to TRIM72KO groups. (C) Scatter plot of whole-lung bacterial burden at Day 2 P.a. injection in WT, TRIM72KO, WT AM to TRIM72KO, and KO AM to TRIM72KO groups. Gray dashed line designates injected bacterial dose; ^ designates mice that have died. P < 0.05 for WT versus TRIM72KO groups, and for WT AM to TRIM72KO versus KO AM to TRIM72KO, n = 6–10 (as described in B). (D) At Day 2 after P.a. injection, ELISA detection of cytokine levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-12, and IL-10 in BALF; total cell number in BALF was measured by hemocytometer counting, n = 5 for WT PBS (open bar), n = 10 for WT P.a. (open bar), and n = 9 for TRIM72KO P.a. (solid bar), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005 compared with WT PBS; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.005 compared with WT P.a. (E) Lung tissue levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-12, and IL-10 in WT AM to TRIM72KO and KO AM to TRIM72KO groups at Day 2 after P.a. injection; n = 6, **P < 0.005. Data are presented as mean (±SE).