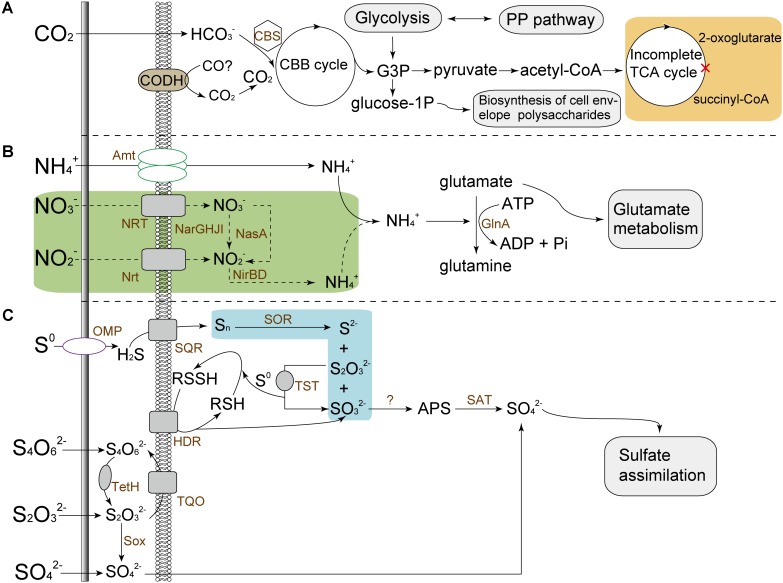
FIGURE 4.
Predicted models for central metabolisms of A. thiooxidans strains, including carbon assimilation (A), nitrogen metabolism (B), and sulfur oxidation (C). In the incomplete TCA cycle (citrate cycle), 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase that catalyzes the transformation of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA was predicted to be absent (orange area), which were also previously reported in some other studies (Zhang et al., 2016a,e). The nitrate reductase (NarGHJI) and nitrite reductase (NirBD) pertaining to dissimilatory nitrate reduction, and putative assimilatory nitrate reductase catalytic subunit (NasA) associated to assimilatory nitrate reduction were predicted to be present in A. thiooxidans species except for ATCC 19377 (green area). For strain ATCC 19377, ammonium was required as an alternative nitrogen source. Unlike other A. thiooxidans strains, a key enzyme sulfur oxygenase reductase (SOR) involved in sulfur oxidation was absent in draft genome of strain ATCC 19377 probably due to the low sequencing depth (blue area). CBS, carboxysome; PP pathway, pentose phosphate pathway; CODH, carbon-monoxide dehydrogenase; CBB cycle, Calvin–Benson–Bassham cycle; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; Amt, ammonia transporter; Nrt, nitrate/nitrite transporter; NRT, nitrate transporter; NarGHJI, nitrate reductase; NirBD, nitrite reductase; NasA, assimilatory nitrate reductase catalytic subunit; GlnA, glutamine synthetase; OMP, outer membrane protein; SQR, sulfide quinone oxidoreductase; TQO, thiosulfate:quinone oxidoreductase; TetH, tetrathionate hydrolase; Sox, sulfur oxidizing protein; TST, thiosulfate sulfurtransferase; HDR, heterodisulfide reductase.