FIGURE 2.
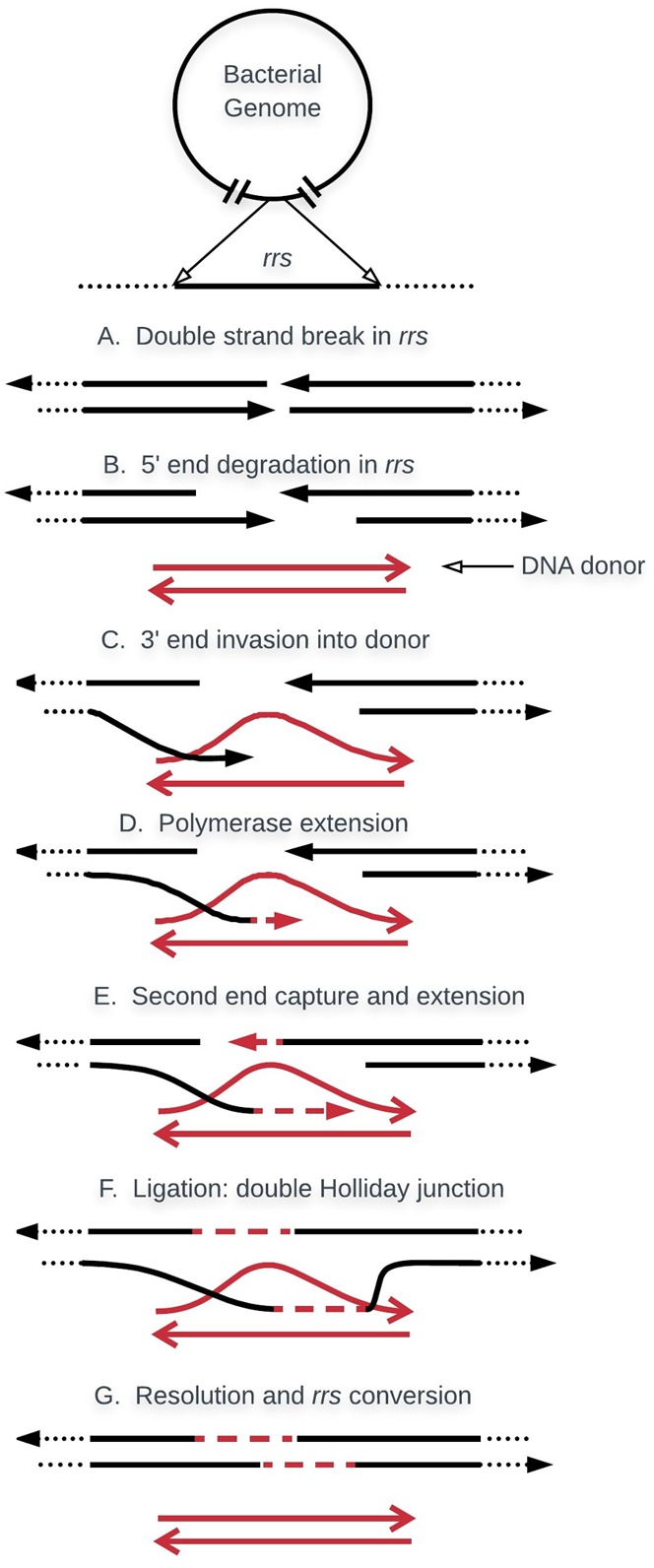
Basic model for gene conversion. In bacteria with multiple copies, rrs evolve in concert by non-reciprocal recombination, where one copy contributes the genome while the other copy provides only a segment of the rrs, or the whole gene. The process is initiated by a DSB in the rrs of the genome (red). This is processed by RecBCD exonuclease/helicase to create a gap and an ssDNA (arrow heads are 3′-ends). RecA promotes strand invasion of the rrs segment. The invading tail then initiates new DNA synthesis which extends until it overlaps and anneals with the other end of the DSB. Through a similar process, the displaced DNA strand forms hDNA with the second 3′-end ssDNA. Two Holliday Junctions are formed which are able to migrate and extend hDNA. Segments of gene conversion can be generated in two different ways. One alternative is through repair, by DNA synthesis, of the gap produced during initiation. The other is through the methyl- directed mismatch repair system which may “repair” hDNA by destroying one strand of DNA in the heteroduplex, followed by new DNA synthesis using the remaining strand as template.
