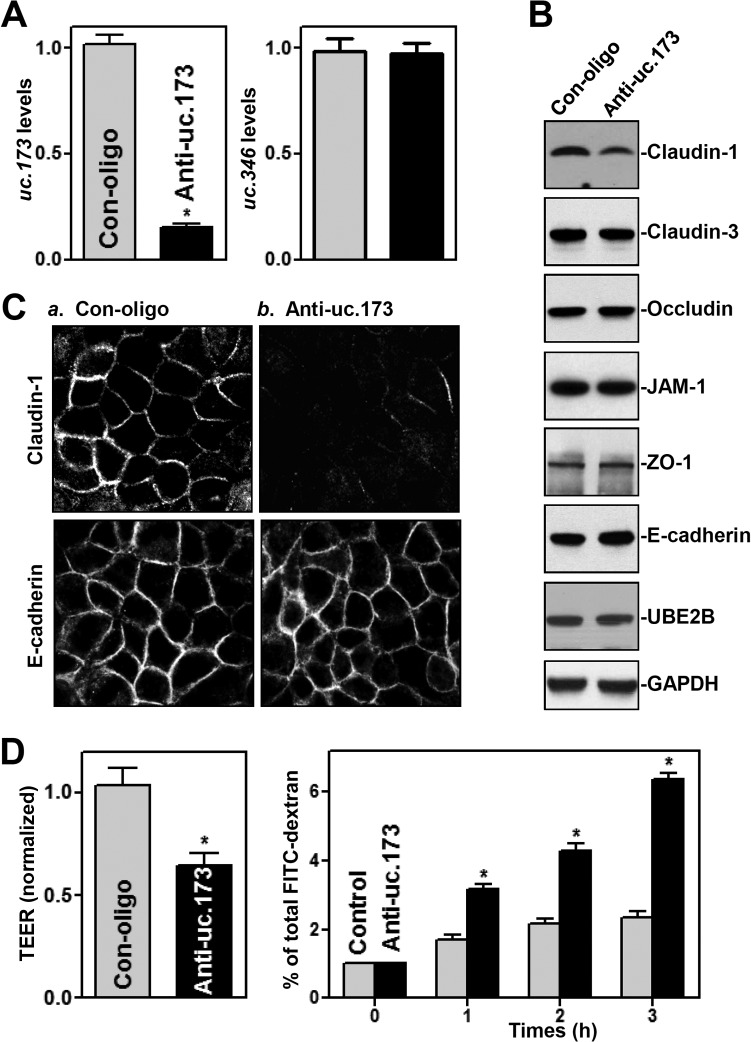
FIG 1.
LNA-mediated uc.173 silencing inhibits claudin-1 expression and disrupts epithelial barrier function. (A) Levels of cellular uc.173 48 h after transfection with LNA-siRNA targeting uc.173 (anti-uc.173) or a control siRNA (Con-oligo) in Caco-2 cells. Values are relative to control levels and are means ± SEM from triplicate experiments. The asterisk indicates a significant difference (P < 0.05) from the Con-oligo result. (B) Representative immunoblots of tight junctions and an adherens junction in cells treated as described for panel A. Three experiments were performed, with similar results. (C) Distribution of claudin-1 and E-cadherin in cells treated as described for panel A. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and incubated first with an antibody against claudin-1 or E-cadherin and then with FITC-conjugated anti-IgG. Original magnification, ×500. (D) Changes in epithelial barrier function, as indicated by changes in TEER (left) and FITC-dextran paracellular permeability (right), in cells treated as described for panel A. TEER assays were performed on 12-mm Transwell filters; paracellular permeability was assayed by adding the membrane-impermeant trace molecule FITC-dextran to the insert medium. Values are means ± SEM of data from six samples. Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) from the Con-oligo results.