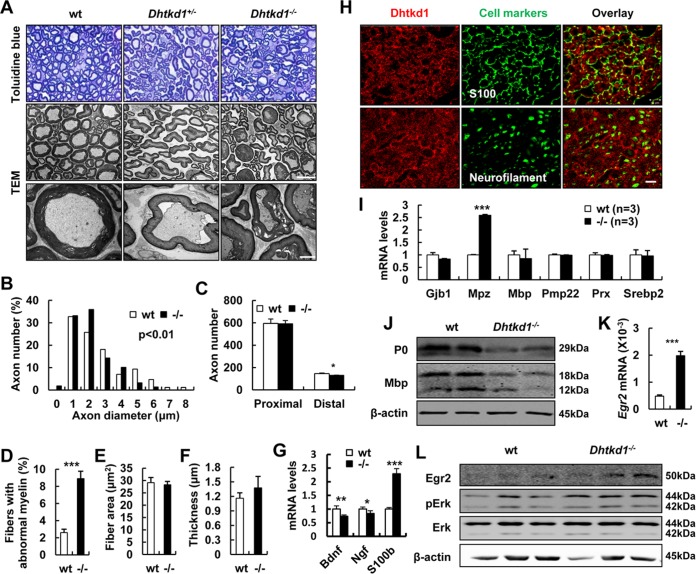
FIG 2.
Aberrant myelin and axon morphology in Dhtkd1−/− sciatic nerves is caused by aberrant P0 expression. (A) Semithin cross sections of sciatic nerves stained with toluidine blue. Magnification, ×1,000. Electron micrographs of sciatic nerves exhibit abnormal myelin fractures and axon degeneration in Dhtkd1−/− mice. Scale bars, 10 μm (middle panel) and 2 μm (bottom panel). (B) Chi-square test (P = 0.003) shows the distribution of axon diameters of the sciatic nerves. (C) Quantification of the number of axons in both proximal and distal parts of the sciatic nerves. (D) The percentage of irregular fiber (index of circularity < 0.75) in Dhtkd1−/− mice and in wt mice (3 mice with 15 fields per group). (E and F) Fiber area and myelin thickness are not changed due to Dhtkd1 deletion. (G) Real-time PCR analysis shows the expression levels of Bdnf, Ngf, and S100b. (H) Expression of DHTKD1 on cryosections of sciatic nerves. Scale bar, 10 μm. (I) Real-time PCR analysis shows the expression levels of central myelin genes in sciatic nerves, including Mpz, myelin basic protein (Mbp), connexin 32 (Gjb1), the peripheral myelin protein 22-kDa gene (PMP22), periaxin (Prx), and sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 (Srebp2). (J) Western blot analysis of P0 and MBP protein levels in sciatic nerves from both wt and Dhtkd1−/− mice. (K) Real-time PCR analysis of Egr2 mRNA expression in sciatic nerves. (L) Western blot analysis of EGR2 protein levels and the ERK signaling pathway in sciatic nerves from both wt and Dhtkd1−/− mice. β-Actin was used as a loading control. A Student two-sided t test was used for data shown in panels C to G, I, and K. Values for all parameters are shown as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.