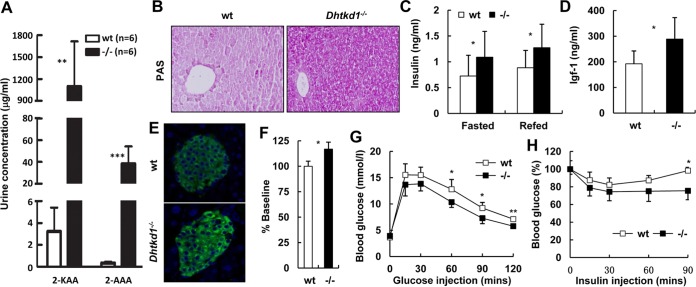
FIG 3.
DHTKD1 deficiency leads to elevated insulin in mice. (A) GC/MS analysis of urinary excretion of 2-AAA and 2-KAA in 16-week-old mice. (B) Periodic acid-Schiff staining of glycogen in liver indicates more glycogen storage in Dhtkd1−/− liver. Magnification, ×200. (C) Serum insulin levels were measured (n = 10 mice per genotype). (D) Dhtkd1−/− mice exhibit increased plasma IGF-1 levels (n = 10 mice per genotype). (E) Immunofluorescence analysis of pancreatic insulin in islets shows elevated insulin in Dhtkd1−/− mice. Magnification, ×200. (F) ELISA of insulin in isolated islets. (G and H) GTT and ITT in wt and Dhtkd1−/− mice (n = 7 or 8 mice per genotype). A Student two-sided t test was used for data in panels A, C, D, F, G, and H. Values are shown as means ± SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.