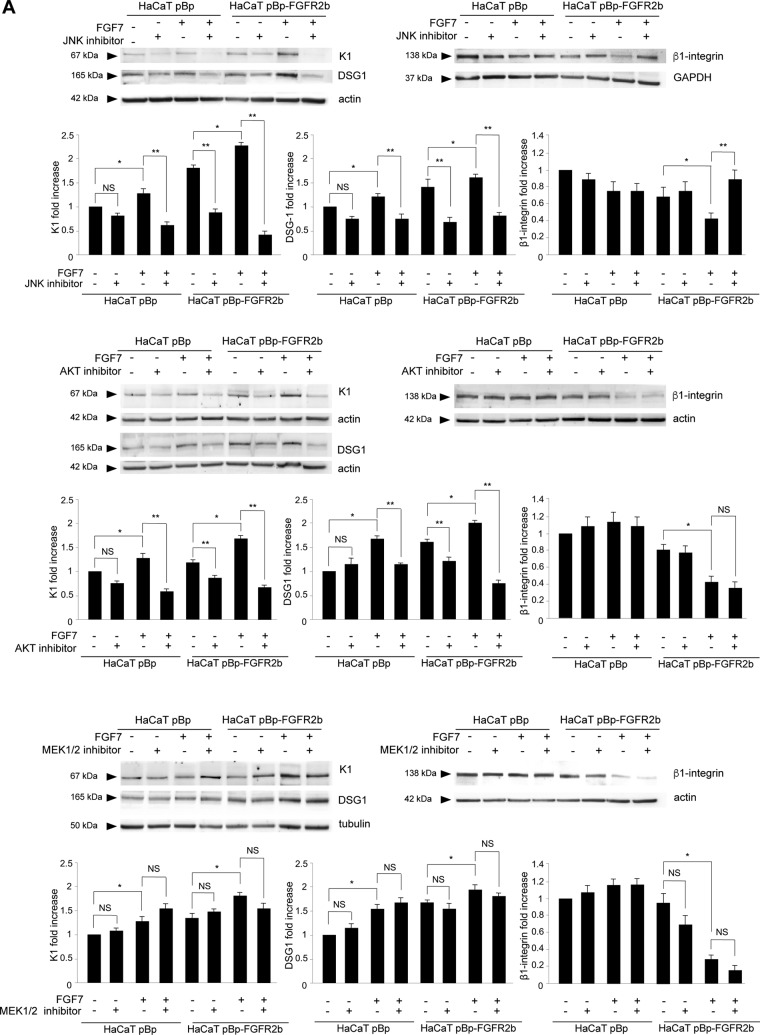
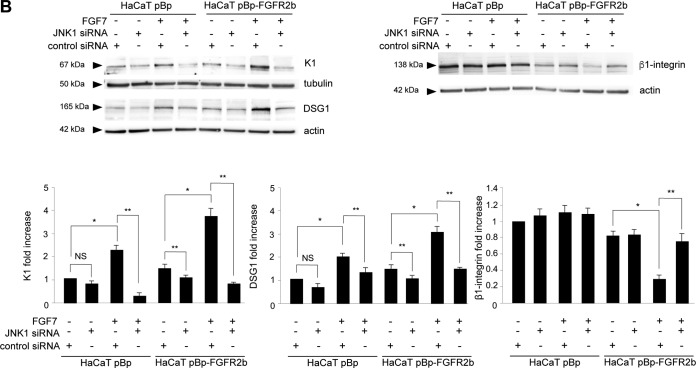
FIG 5.
JNK1 signaling is involved in FGFR2b-triggered early differentiation. (A) HaCaT pBp and HaCaT pBp-FGFR2b cells were left untreated or stimulated with FGF7 in the presence or absence of the indicated substrate inhibitors as described in Materials and Methods. Western blot analysis shows that the JNK inhibitor strongly impairs the increases in K1 and DSG1 and the repression of β1-integrin induced by FGF7 stimulation, while the AKT inhibitor shows an inhibitory effect only on FGF7-induced up-modulation of K1 and DSG1, and not on β1-integrin reduction. The MEK1/2 inhibitor does not display any effect on the differentiation marker modulation induced by FGF7. Equal loading was assessed with antiactin, antitubulin, and anti-GAPDH antibodies. Densitometric analysis and Student's t test were performed as reported in the legend to Fig. 2. *, P < 0.05 versus the results for the corresponding FGF7-unstimulated cells. For comparison to the results for the corresponding substrate inhibitor-untreated cells: **, P < 0.05; NS, not significant. (B) HaCaT pBp and HaCaT pBp-FGFR2b clones were transiently transfected with JNK1 siRNA or an unrelated siRNA as a control. Cells were then left untreated or stimulated with FGF7 as described in Materials and Methods. Western blot analysis shows that JNK1 silencing strongly damps the increases in K1 and DSG1 and rescues the repression of β1-integrin induced by FGF7 stimulation. Equal loading was assessed with antiactin antibody. Densitometric analysis and Student's t test were performed as reported in the legend to Fig. 2. *, P < 0.05 versus the results for the corresponding FGF7-unstimulated cells. For comparison to the results for the corresponding control siRNA cells: **, P < 0.05; NS, not significant.