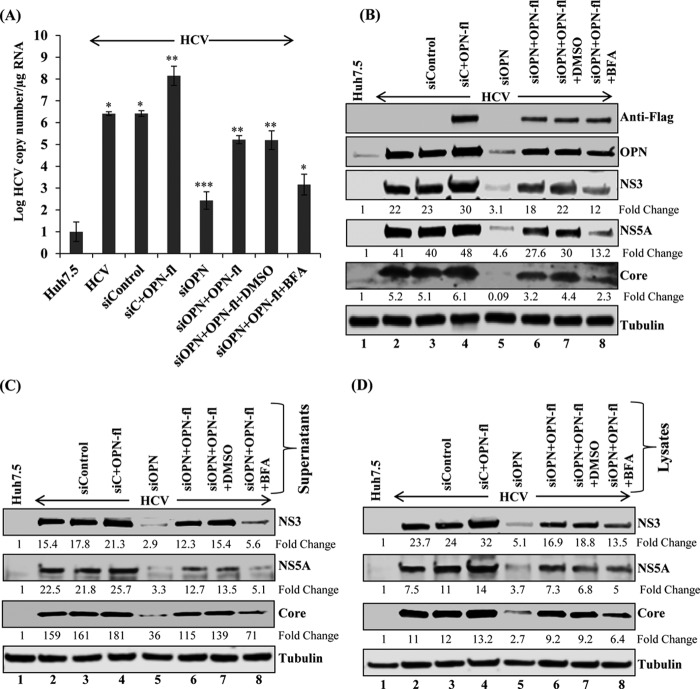
FIG 4.
OPN overexpression rescues HCV RNA replication, HCV infectivity, and assembly. (A) HCV-infected Huh7.5 cells (day 4) were transfected with sicontrol, sicontrol plus Flag-tagged OPN (OPN-fl), siOPN, and siOPN plus OPN-fl. At 48 h posttransfection, cells transfected with siOPN plus OPN-fl were incubated with DMSO and BFA (40 ng/ml) for 8 h. The cells were washed and replaced with fresh medium for 16 additional hours to complete 72 h of transfection. Total RNA was extracted and HCV copy number was analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR. Data represent means ± SDs from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. *, P < 0.05 compared to mock-infected Huh7.5 cells, as well as cells transfected with siOPN plus OPN-fl plus DMSO versus siOPN plus OPN-fl plus BFA. **, P < 0.01 compared to HCV-infected Huh7.5 cells transfected with control vector and sicontrol, as well as cells transfected with siOPN versus siOPN plus OPN-fl; ***, P < 0.001 compared to HCV-infected Huh7.5 cells transfected with sicontrol. (B) Equal amounts of cellular lysates from panel A were immunoblotted using anti-Flag, anti-OPN, anti-NS5A, anti-NS3, and anti-tubulin antibodies. (C) The cell culture supernatants collected for panel A were incubated with naive Huh7.5 cells as described for Fig. 2. At day 3 postinfection, the cellular lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (D) The harvested cells from panel A were resuspended in DMEM with 10% FCS and lysed by freeze-thaw cycling as described for Fig. 2. The collected supernatants were incubated with naive Huh7.5 cells for 6 h. At day 3 postinfection, equal amounts of cellular lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Tubulin was used as a protein loading control.