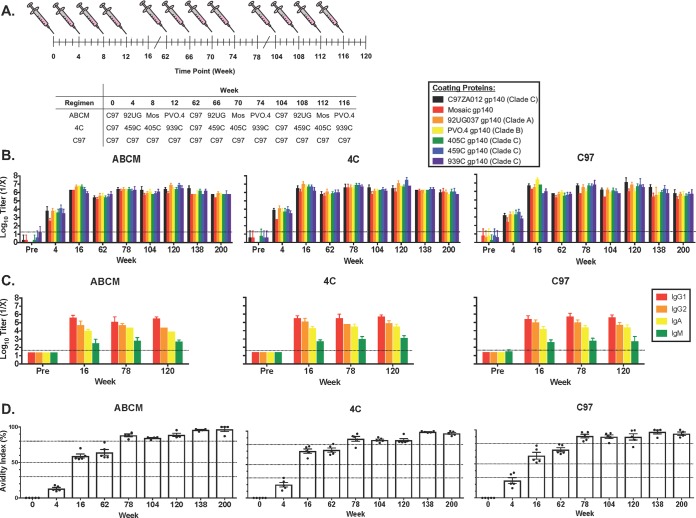
FIG 1.
Vaccination regimens and characterization of binding antibody responses. (A) Vaccination regimens for guinea pigs immunized with a longitudinal prime/boost vaccination schedule. Animals were vaccinated at weeks 0, 4, 8, 12, 62, 66, 70, 74, 104, 108, 112, and 116 utilizing the listed vaccination regimens and bled 4 weeks after each vaccination, as well as at weeks 138 and 200. C97, C97ZA012 gp140; 92UG, 92UG037 gp140; Mos, mosaic gp140. Error bars represent the standard deviations. (B) Binding antibody titers for HIV-1 Env gp140s of different clades as measured by endpoint ELISAs. (C) Binding antibody titers for HIV-1 C97ZA012 gp140, showing specific isotype and subclass responses, as measured utilizing endpoint ELISAs. Error bars represent the standard deviations. (D) Guinea pig polyclonal antibody avidity as measured by urea disruption ELISA. Each dot represents the result for an individual animal, and error bars represent the standard deviations. Percent avidity was calculated using the following formula: [(absorbance of urea-treated sample/absorbance of non-urea-treated matched sample) × 100]. Zero to 30% is low avidity, 30 to 50% is moderate avidity, and >50% is high avidity. The 80% bar is used as a reference point within the high-avidity region.