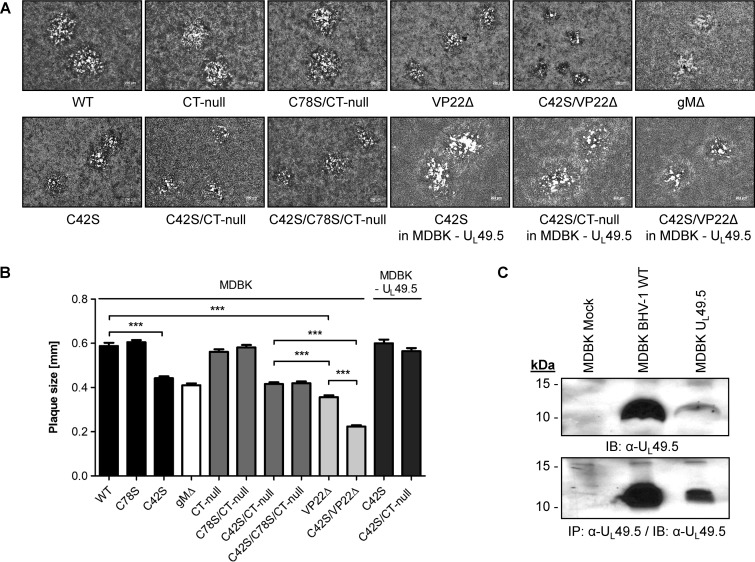
FIG 3.
Plaque morphology of BHV-1 UL49.5 mutants in MDBK cells and MDBK cells expressing wt UL49.5. (A) Representative images of plaque morphology of BHV-1 wt, UL49.5 CT-null, C42S, C78S/CT-null, C42S/CT-null, C42S/C78S/CT-null, VP22Δ, C42S/VP22Δ, and gMΔ viruses in MDBK cells. For comparison, plaque morphologies of C42S, double mutant C42S/CT-null, and double mutant C42S/VP22Δ viruses produced in the wt UL49.5-expressing MDBK cell line (UL49.5-MDBK) are shown. Plaque sizes were measured at 48 hpi. (B) Bar graph showing comparative plaque sizes produced by BHV-1 wt, UL49.5 C78S, C42S, gMΔ, CT-null, C78S/CT-null, C42S/CT-null, C42S/C78S/CT-null, VP22Δ, and C42S/VP22Δ viruses. For comparison, plaque sizes produced by UL49.5 C42S and double mutant C42S/CT-null viruses in a wt UL49.5-expressing MDBK cell line (UL49.5-MDBK) are shown. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. ***, P < 0.001. (C) Analysis of UL49.5 expression in a stable MDBK UL49.5-expressing cell line compared with the level in wt virus-infected MDBK cells, as determined by immunoblotting (IB) or by immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-UL49.5 antibody.