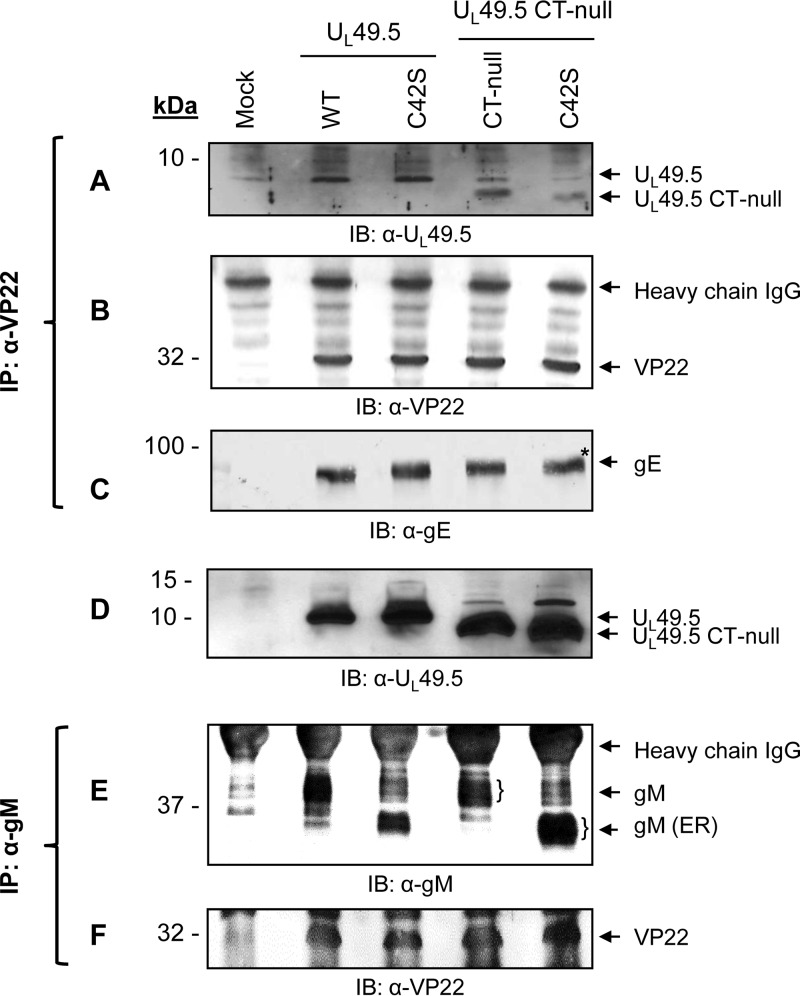
FIG 7.
Analysis of UL49.5-VP22 and gM-VP22 interactions by coimmunoprecipitation. Infected cell lysates of mock, BHV-1 wt, C42S, CT-null, and C42S/CT-null viruses were immunoprecipitated with anti-VP22 antibody. Immunoprecipitated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, and Western blotting of membranes from the identical gels was performed with anti-UL49.5 (A), anti-VP22 (B), and anti-gE (C) antibodies. The levels of VP22 and gE immunoprecipitated and/or coimmunoprecipitated, respectively, with the anti-VP22 antibody from wt and mutant UL49.5 virus-infected cell lysates and visualized by anti-VP22 and anti-gE antibodies served as loading controls. (D) As a cell lysate control, an immunoblot developed with anti-UL49.5-specific antibody of mock-, BHV-1 wt-, and mutant UL49.5-infected cell lysates is shown. (E and F) Infected cell lysates of mock, BHV-1 wt, C42S, CT-null, and C42S/CT-null viruses were immunoprecipitated with anti-gM antibody. Western blotting of the immunoprecipitated proteins was performed with anti-gM-specific and anti-VP22-specific antibodies.