FIG 8.
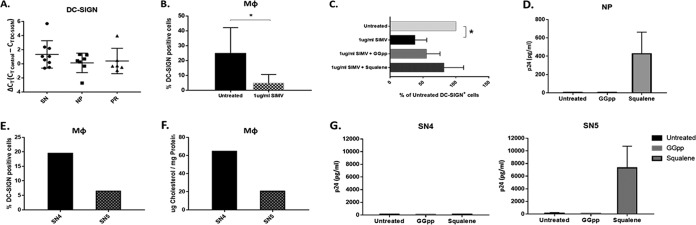
SIMV decreases the number of DC-SIGN+ MΦ and trans infection in a cholesterol-dependent manner. (A) Total RNA extracted from SN, NP, and PR MΦ was used to measure DC-SIGN gene expression by RT-PCR. The cycle threshold (CT) of the DC-SIGN probe was subtracted from the CT of the RNA polymerase II probe within each sample for a relative ΔCT value. (B) SN MΦ were left untreated or were treated with 1 μg/ml SIMV (n = 5) or in the presence of SIMV and GGpp or SIMV and squalene (C) for 24 h prior to analysis of DC-SIGN surface expression by flow cytometry (n = 4). (D) p24 level on day 12 of trans infection with untreated NP MΦ, NP MΦ treated with GGpp for 24 h, or NP MΦ treated with squalene for 24 h (n = 3). (E and F) Percentage of DC-SIGN+ MΦ (E) and total cholesterol (F) of participants SN4 and SN5. (G) p24 level on day 12 of trans infection with untreated SN4 and SN5 MΦ, SN4 and SN5 MΦ treated with GGpp for 24 h, or SN4 and SN5 MΦ treated with squalene for 24 h (two independent experiments). *, P ≤ 0.05. Histograms represent the means ± SE.