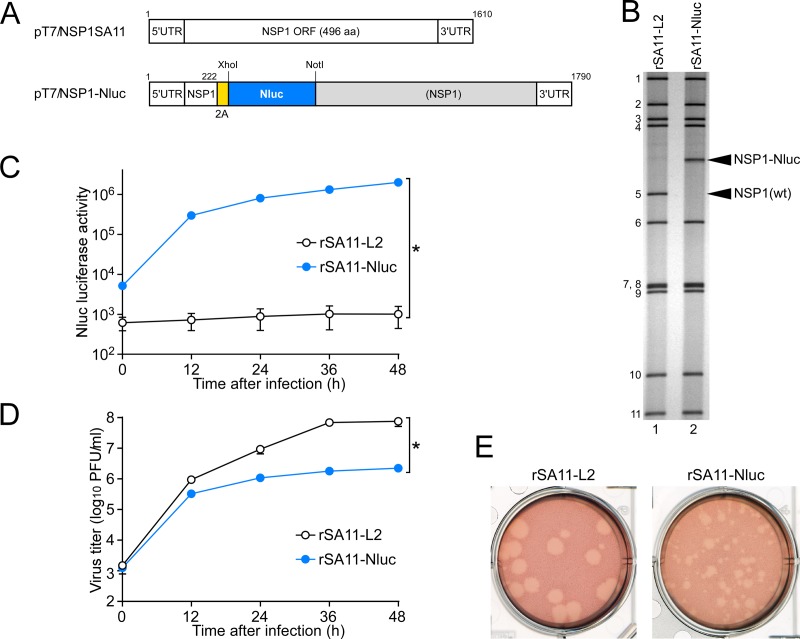
FIG 3.
Generation of recombinant rSA11-Nluc virus expressing Nluc luciferase. (A) Schematic presentation of the plasmids carrying the NSP1 genes for rescue of the wild-type (wt) rSA11-L2 and rSA11-Nluc viruses (pT7/NSP1SA11 and pT7/NSP1-Nluc, respectively). To generate plasmid pT7/NSP1-Nluc, nucleotides 223 to 643 in the NSP1 ORF were replaced with the 2A-Nluc gene. (B) PAGE of viral genomic dsRNAs extracted from rSA11-L2 and rSA11-Nluc. Lane 1, dsRNAs from rSA11-L2; lane 2, dsRNAs from rSA11-Nluc. The numbers on the left indicate the order of the genomic dsRNA segments of rSA11-L2. (C) Nluc luciferase activities of rSA11-L2 and rSA11-Nluc. MA104 cells were infected with rSA11-L2 or rSA11-Nluc at an MOI of 0.01 and then incubated for various numbers of hours. Nluc activities in the cultures were determined by luminometry. The data shown are the mean Nluc activities and standard deviations (SDs) for three independent cell cultures. *, P < 0.05 (as determined by t test). (D) Multiple-step growth curves for rSA11-L2 and rSA11-Nluc. MA104 cells were infected with rSA11-L2 or rSA11-Nluc at an MOI of 0.01 and then incubated for various numbers of hours. Virus titers in the cultures were determined by plaque assay. The data shown are the mean viral titers and SDs for three independent cell cultures. *, P < 0.05 (as determined by t test). (E) Plaque formation by rSA11-L2 and rSA11-Nluc. rSA11-L2 or rSA11-Nluc was directly plated onto CV-1 cells for plaque formation. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results, and representative results are shown.