The synthesis and crystal structure of a new thiophene monomer containing a 1,2,4-triazole-5-thione ring are reported. The thiophene and 1,2,4-triazole rings are inclined to each other by 79.70 (9)°.
Keywords: crystal structure; thiophene; 1,2,4-triazole; thione tautomer; Hirshfield surfaces
Abstract
In the title compound, C13H11N3S2, the phenyl ring is twisted from the 1,2,4-triazole plane by 63.35 (9)° and by 47.35 (9)° from the thiophene plane. In the crystal, chains of molecules running along the c-axis direction are formed by N—H⋯S interactions [graph-set motif C(4)]. The 1,2,4-triazole and phenyl rings are involved in π–π stacking interactions [centroid–centroid distance = 3.4553 (10) Å]. The thiophene ring is involved in C—H⋯S and C—H⋯π interactions. The intermolecular interactions in the crystal packing were further analysed using Hirshfield surface analysis, which indicates that the most significant contacts are H⋯H (35.8%), followed by S⋯H/H⋯S (26.7%) and C⋯H/H⋯C (18.2%).
Chemical context
The triazole ring is an important component of bioactive heterocycles because of its effect in bactericides, pesticides and fungicides (Sengupta et al., 1978 ▸; Singh et al., 1979 ▸; Giri et al., 1978 ▸). Many derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazoline-5-thione show a variety of biological activities: anti-inflamatory (Sahin et al., 2001 ▸), antifungal (Knight et al., 1978 ▸, 1979 ▸), analgesis (Mekuskiene et al., 1998 ▸) and bacteriostatic (Eweiss et al., 1986 ▸; Mazzone et al., 1981 ▸). Thiophene-containing 1,2,4-triazole derivatives have been studied and these compounds have shown promising antimycotic activity (Wujec et al., 2004 ▸). Combinations of the thiophene ring with other heterocyclic rings applied in conducting polymers have also been investigated (Ho et al., 2002 ▸; Mohamed et al., 2014 ▸; Bondarev et al., 2010 ▸).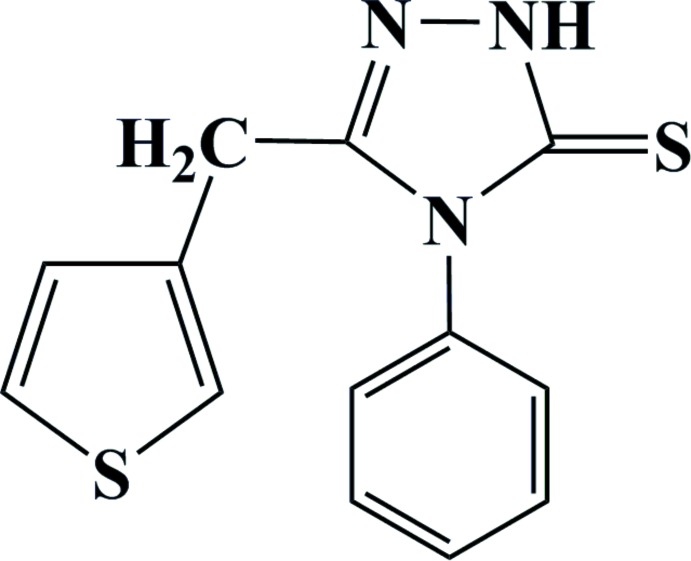
As part of our studies, we have synthesized a new thiophene monomer containing 1,2,4-triazole-5-thione. The polymer obtained from 4-phenyl-3-(thiophen-3-yl-methyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione was further characterized by IR spectroscopy and TGA. TG–TGA analysis shows that the polymer is thermally stable above 473 K, showing degradation beyond 773 K and exothermic maxima at 745 K. We present here the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
Structural commentary
The title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸). In the crystalline state, the central 1,2,4-triazole ring exists in its thione tautomeric state with a C2=S1 distance of 1.6845 (16) Å. The short C4=N5 distance [1.302 (2) Å] indicates its double-bond character. The 1,2,4-triazole ring is almost planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.002 Å for ring C2/N3/C4/N5/N6), with the substituents S1, C7 and C13 deviating by −0.020 (1), −0.028 (2) and 0.061 (2) Å, respectively. The plane of the 1,2,4-triazole ring forms dihedral angles of 79.70 (9) and 63.35 (9)° with the best planes through the thiophene and phenyl rings, respectively. The thiophene and phenyl rings are inclined to each other by 47.35 (9)°. The thiophene ring does not show rotational disorder as observed in previous structure determinations of similar compounds (Vu Quoc et al., 2017 ▸).
Figure 1.
View of the asymmetric unit of the title compound, showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as small circles of arbitrary radii.
Supramolecular features
The crystal packing of the title compound is shown in Fig. 2 ▸. The packing is dominated by N6—H6⋯S1 interactions (Table 1 ▸), resulting in the formation of chains of molecules with graph-set motif C(4) propagating along the c-axis direction. In addition, the 1,2,4-triazole and phenyl rings exhibit π–π stacking interactions [Cg2⋯Cg3i = 3.4553 (10) Å; angle of inclination = 9.98 (9)°; Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the 1,2,4-triazole and phenyl rings, respectively; symmetry code: (i) x, −y +  , z +
, z +  ; Fig. 2 ▸].
; Fig. 2 ▸].
Figure 2.
Crystal packing of the title compound shown in projection down the a axis illustrating chain formation along the c-axis direction by N—H⋯S hydrogen bonding (yellow dashed lines) and the π–π stacking interactions between the 1,2,4-triazole (yellow) and phenyl (blue) rings.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C14/C15/S16/C17/C18 thiophene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N6—H6⋯S1i | 0.88 | 2.46 | 3.2866 (16) | 156 |
| C8—H8⋯S16ii | 0.95 | 2.82 | 3.737 (2) | 162 |
| C10—H10⋯Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.83 | 3.566 (2) | 135 |
| C13—H13B⋯Cg1iv | 0.99 | 2.76 | 3.409 (2) | 123 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
The thiophene ring plays also a role in the crystal packing as illustrated by the weaker C8—H8⋯S16 interactions and C—H⋯π interactions involving H atoms H10 and H13B (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 3 ▸). The crystal packing contains no voids.
Figure 3.
Partial crystal packing of the title compound, showing the C—H⋯π (gray dashed lines) and C—H⋯S interactions (yellow dashed lines) [see Table 1 ▸; symmetry codes: (i) x, y, z + 1; (ii) −x + 2, −y + 1, −z + 1; (iii) x − 1, y, z − 1; (iv) x + 1, y, z + 1].
Hirshfield surface analysis
Hirshfield surface and two-dimensional fingerprint plot calculations were performed using CrystalExplorer (McKinnon et al., 2007 ▸; Spackman & Jayatilaka, 2009 ▸). The larger bright-red spots near atoms S1, N6, S16 and H8 (labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4) on the Hirshfield surface mapped over d norm in Fig. 4 ▸ a and b represent the N—H⋯S and C—H⋯S hydrogen bonds present in the crystal packing. The pale-red spots in Fig. 4 ▸ a near atom N5 and the phenyl ring (labelled 5 and 6) are the result of the π–π stacking between the 1,2,4-triazole and phenyl rings. In Fig. 4 ▸ b, an additional pale-red spot is present near atom S16 (labelled 7), indicating a short S⋯S contact [S16⋯S16i = 3.4688 (7) Å; symmetry code: (i) −x + 2, −y + 1, −z + 2]. The relative contributions of the different intermolecular interactions to the Hirshfield surface area, in descending order, are: H⋯H (35.8%), S⋯H/H⋯S (26.7%), C⋯H/H⋯C (18.2%), N⋯H/H⋯N (8.5%), C⋯N/N⋯C (3.7%), C⋯C (3.1%), S⋯C/C⋯S (2.8%) and S⋯S (1.2%). The latter value indicates that the S⋯S contact only makes a marginal contribution to the packing of the title compound.
Figure 4.
Two views of the Hirshfield surface for the title compound mapped over d norm in the range −0.386 to +1.111 a.u., showing (a) the N—H⋯S and C—H⋯S hydrogen bonding and π–π interactions between the 1,2,4-triazole and phenyl rings, and (b) the N—H⋯S and C—H⋯S hydrogen bonding and S⋯S interactions.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.39, last update November 2017; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for crystal structures containing a 1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione moiety results in 287 (only organics) or 375 structures (including organometallics). When considering only organics, the average C=S and C=N distances are, respectively, 1.676 (9) Å [ranging from 1.608 to 1.699 Å] and 1.302 (11) Å [ranging from 1.275 to 1.410 Å]. For the 66 structures with atom N3 bearing a phenyl subsituent (only organics), the dihedral angle between the 1,2,4-triazole and phenyl rings varies from 55.3 to 90° (the latter when bulky substituents are present at position C4). In the case of a –CH2 R group at position C4, 53 structures are retrieved from the CSD. In this case, the torsion angle N=C—CH2—R shows three favoured regions: (1) synperiplanar for small subsituents (torsion angles between −23 and +32°, 28 hits), (2) +anticlinal (torsion angles between 67 and 115°, 15 hits) and (3) −anticlinal (torsion angles between −87 and −140°, 10 hits).
Synthesis and crystallization
The reaction scheme used to synthesize the title compound, (3), is given in Fig. 5 ▸. Methyl 2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetate, (1), and 2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide, (2), were synthesized as described in a previous study (Vu Quoc et al., 2017 ▸).
Figure 5.
Reaction scheme for the title compound.
A mixture of hydrazide (2) (0.01 mol), phenylisothiocyanate (0.01 mol) and 20 mL ethanol was refluxed at 353 K for 8h. The solid precipitate was filtered, washed and recrystallized from ethanol to give white crystals (m.p. 416 K). Then, the mixture of the resulting solid (0.411 g), 10 mL ethanol and NaOH 10% (1.25 mmol) was refluxed at 353 K for 3 h. The reaction mixture was cooled and neutralized with HCl 10% to pH = 1–2. The product was filtered, washed and recrystallized from ethanol to give 1.42 g (yield 52%) of (3) in the form of pale-yellow crystals (m.p. 451 K). IR (Nicolet Impact 410 FTIR, KBr, cm−1): 3453 (NH), 3088, 2911 (CH), 1576 (C=C thiophene), 1278, 1207 (C=S). 1H NMR [Bruker XL-500, 500 MHz, d 6-DMSO, δ (ppm), J (Hz)]: 6.96 (m, 1H, H2), 6.75 (d, 1H, 5 J = 4.5, H4), 7.38 (dd, 1H, 2 J = 3.0, 4 J = 5.0, H5), 3.85 (s, 2H, H6), 13.77 (s, 1H, H8), 7.26–7.28 (m, 2H, H11 and H15), 7.48–7.50 (m, 3H, H12, H13 and H14). 13C NMR [Bruker XL-500, 125 MHz, d 6-DMSO, δ (ppm)]: 123.86 (C2), 134.24 (C3), 128.02 (C4), 126.14 (C5), 26.35 (C6), 150.83 (C7), 167.85 (C9), 133.55 (C10), 128.16 (C11 and C15), 129.20 (C12 and C14), 129.34 (C13). Calculation for C13H11N3S2: M = 273 a.u.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The H atoms were placed at calculated positions and refined in riding mode, with a N—H distance of 0.88 Å or C—H distances of 0.95 (aromatic) and 0.99 Å (CH2), and isotropic displacement parameters equal to 1.2U eq of the parent atoms.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C13H11N3S2 |
| M r | 273.37 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.8257 (8), 16.0776 (16), 9.7437 (9) |
| β (°) | 116.383 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1238.6 (2) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.41 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.31 × 0.21 × 0.09 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 Quest CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.700, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 20908, 3082, 2697 |
| R int | 0.038 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.668 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.035, 0.097, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 3082 |
| No. of parameters | 163 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.59, −0.38 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018007193/zp2029sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018007193/zp2029Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018007193/zp2029Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1843042
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C13H11N3S2 | F(000) = 568 |
| Mr = 273.37 | Dx = 1.466 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.8257 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 9914 reflections |
| b = 16.0776 (16) Å | θ = 2.9–28.3° |
| c = 9.7437 (9) Å | µ = 0.41 mm−1 |
| β = 116.383 (3)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1238.6 (2) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.31 × 0.21 × 0.09 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 Quest CMOS diffractometer | 2697 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.038 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 2.9° |
| Tmin = 0.700, Tmax = 0.746 | h = −11→11 |
| 20908 measured reflections | k = −21→21 |
| 3082 independent reflections | l = −12→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.035 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.097 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0467P)2 + 1.0177P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3082 reflections | Δρmax = 0.59 e Å−3 |
| 163 parameters | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.24329 (5) | 0.74179 (3) | 0.05131 (5) | 0.01795 (11) | |
| C2 | 0.40447 (19) | 0.69570 (10) | 0.19985 (17) | 0.0138 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.54765 (16) | 0.65826 (8) | 0.20563 (14) | 0.0132 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.64077 (19) | 0.62860 (10) | 0.35345 (17) | 0.0141 (3) | |
| N5 | 0.56488 (17) | 0.64436 (8) | 0.43857 (15) | 0.0158 (3) | |
| N6 | 0.42054 (16) | 0.68568 (8) | 0.34200 (15) | 0.0151 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.345269 | 0.703954 | 0.371018 | 0.018* | |
| C7 | 0.59244 (19) | 0.64996 (9) | 0.08099 (17) | 0.0130 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.4894 (2) | 0.60295 (10) | −0.04588 (18) | 0.0184 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.390920 | 0.576602 | −0.050509 | 0.022* | |
| C9 | 0.5328 (2) | 0.59507 (11) | −0.16594 (19) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.462216 | 0.563899 | −0.254176 | 0.028* | |
| C10 | 0.6780 (2) | 0.63219 (11) | −0.1584 (2) | 0.0225 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.707029 | 0.626318 | −0.240840 | 0.027* | |
| C11 | 0.7808 (2) | 0.67794 (11) | −0.02992 (19) | 0.0201 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.881215 | 0.702779 | −0.023979 | 0.024* | |
| C12 | 0.7379 (2) | 0.68777 (10) | 0.09068 (18) | 0.0163 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.807211 | 0.719883 | 0.178022 | 0.020* | |
| C13 | 0.8089 (2) | 0.58721 (11) | 0.40650 (18) | 0.0183 (3) | |
| H13A | 0.891635 | 0.627925 | 0.403638 | 0.022* | |
| H13B | 0.799421 | 0.541364 | 0.335289 | 0.022* | |
| C14 | 0.87343 (19) | 0.55283 (10) | 0.56653 (18) | 0.0154 (3) | |
| C15 | 1.0020 (2) | 0.58833 (10) | 0.69147 (18) | 0.0174 (3) | |
| H15 | 1.058440 | 0.638022 | 0.687921 | 0.021* | |
| S16 | 1.04926 (5) | 0.53259 (3) | 0.85492 (5) | 0.02086 (12) | |
| C17 | 0.89607 (19) | 0.45897 (10) | 0.76090 (17) | 0.0150 (3) | |
| H17 | 0.872539 | 0.412045 | 0.807510 | 0.018* | |
| C18 | 0.8116 (2) | 0.47912 (11) | 0.60493 (19) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| H18 | 0.721852 | 0.446760 | 0.532024 | 0.024* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.01244 (19) | 0.0249 (2) | 0.0173 (2) | 0.00407 (14) | 0.00726 (15) | 0.00491 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0135 (7) | 0.0139 (7) | 0.0161 (7) | −0.0021 (5) | 0.0084 (6) | −0.0012 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0155 (6) | 0.0117 (6) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0066 (5) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0159 (7) | 0.0148 (7) | 0.0115 (7) | −0.0002 (5) | 0.0061 (6) | 0.0009 (5) |
| N5 | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0146 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0073 (5) | 0.0016 (5) |
| N6 | 0.0147 (6) | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0154 (6) | 0.0019 (5) | 0.0091 (5) | 0.0001 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0141 (7) | 0.0147 (7) | 0.0120 (6) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0073 (5) | 0.0024 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0163 (7) | 0.0208 (8) | 0.0164 (7) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0058 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0274 (9) | 0.0267 (9) | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0019 (7) | 0.0075 (7) | −0.0030 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0284 (9) | 0.0267 (9) | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0108 (7) | 0.0150 (7) | 0.0061 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0185 (7) | 0.0235 (8) | 0.0226 (8) | 0.0049 (6) | 0.0132 (7) | 0.0083 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0154 (7) | 0.0182 (8) | 0.0151 (7) | 0.0013 (6) | 0.0067 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0238 (8) | 0.0143 (7) | 0.0070 (6) | 0.0087 (6) | 0.0053 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0157 (7) | 0.0178 (7) | 0.0137 (7) | 0.0046 (6) | 0.0073 (6) | 0.0028 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0179 (7) | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0165 (7) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0080 (6) | 0.0023 (6) |
| S16 | 0.0193 (2) | 0.0267 (2) | 0.0146 (2) | −0.00099 (16) | 0.00573 (16) | 0.00087 (15) |
| C17 | 0.0129 (7) | 0.0168 (7) | 0.0132 (7) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0038 (6) | −0.0004 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0213 (8) | 0.0159 (7) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0058 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C2 | 1.6845 (16) | C10—C11 | 1.386 (3) |
| C2—N3 | 1.378 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C2—N6 | 1.338 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.395 (2) |
| N3—C4 | 1.3876 (19) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C7 | 1.4407 (19) | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C4—N5 | 1.302 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C13 | 1.494 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.507 (2) |
| N5—N6 | 1.3727 (18) | C14—C15 | 1.367 (2) |
| N6—H6 | 0.8800 | C14—C18 | 1.423 (2) |
| C7—C8 | 1.388 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C12 | 1.385 (2) | C15—S16 | 1.7098 (16) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | S16—C17 | 1.7226 (16) |
| C8—C9 | 1.389 (2) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | C17—C18 | 1.401 (2) |
| C9—C10 | 1.386 (3) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9500 | ||
| N3—C2—S1 | 129.51 (12) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| N6—C2—S1 | 127.09 (12) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.48 (16) |
| N6—C2—N3 | 103.39 (13) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| C2—N3—C4 | 107.58 (13) | C7—C12—C11 | 118.91 (15) |
| C2—N3—C7 | 126.59 (13) | C7—C12—H12 | 120.5 |
| C4—N3—C7 | 125.83 (13) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.5 |
| N3—C4—C13 | 123.47 (14) | C4—C13—H13A | 109.1 |
| N5—C4—N3 | 111.06 (14) | C4—C13—H13B | 109.1 |
| N5—C4—C13 | 125.43 (14) | C4—C13—C14 | 112.45 (13) |
| C4—N5—N6 | 103.95 (12) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.8 |
| C2—N6—N5 | 114.02 (13) | C14—C13—H13A | 109.1 |
| C2—N6—H6 | 123.0 | C14—C13—H13B | 109.1 |
| N5—N6—H6 | 123.0 | C15—C14—C13 | 123.41 (15) |
| C8—C7—N3 | 118.99 (14) | C15—C14—C18 | 112.18 (14) |
| C12—C7—N3 | 119.67 (14) | C18—C14—C13 | 124.39 (15) |
| C12—C7—C8 | 121.33 (15) | C14—C15—H15 | 124.1 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.6 | C14—C15—S16 | 111.90 (12) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 118.88 (16) | S16—C15—H15 | 124.1 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.6 | C15—S16—C17 | 93.21 (8) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.6 | S16—C17—H17 | 125.3 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.70 (16) | C18—C17—S16 | 109.37 (12) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.6 | C18—C17—H17 | 125.3 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.2 | C14—C18—H18 | 123.3 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 119.68 (16) | C17—C18—C14 | 113.35 (14) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.2 | C17—C18—H18 | 123.3 |
| S1—C2—N3—C4 | −179.20 (12) | N6—C2—N3—C4 | −0.37 (16) |
| S1—C2—N3—C7 | −0.1 (2) | N6—C2—N3—C7 | 178.76 (14) |
| S1—C2—N6—N5 | 178.97 (11) | C7—N3—C4—N5 | −178.60 (14) |
| C2—N3—C4—N5 | 0.55 (18) | C7—N3—C4—C13 | 3.6 (2) |
| C2—N3—C4—C13 | −177.23 (15) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 1.1 (3) |
| C2—N3—C7—C8 | −63.5 (2) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −0.1 (2) |
| C2—N3—C7—C12 | 117.40 (17) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.2 (3) |
| N3—C2—N6—N5 | 0.10 (17) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.9 (3) |
| N3—C4—N5—N6 | −0.46 (17) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 1.0 (2) |
| N3—C4—C13—C14 | −173.79 (14) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −1.0 (2) |
| N3—C7—C8—C9 | 179.97 (15) | C13—C4—N5—N6 | 177.26 (15) |
| N3—C7—C12—C11 | 178.94 (14) | C13—C14—C15—S16 | −178.12 (12) |
| C4—N3—C7—C8 | 115.47 (17) | C13—C14—C18—C17 | 178.09 (15) |
| C4—N3—C7—C12 | −63.6 (2) | C14—C15—S16—C17 | −0.21 (13) |
| C4—N5—N6—C2 | 0.22 (18) | C15—C14—C18—C17 | −0.4 (2) |
| C4—C13—C14—C15 | −106.27 (18) | C15—S16—C17—C18 | −0.01 (13) |
| C4—C13—C14—C18 | 75.4 (2) | S16—C17—C18—C14 | 0.22 (18) |
| N5—C4—C13—C14 | 8.8 (2) | C18—C14—C15—S16 | 0.37 (18) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C14/C15/S16/C17/C18 thiophene ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N6—H6···S1i | 0.88 | 2.46 | 3.2866 (16) | 156 |
| C8—H8···S16ii | 0.95 | 2.82 | 3.737 (2) | 162 |
| C10—H10···Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.83 | 3.566 (2) | 135 |
| C13—H13B···Cg1iv | 0.99 | 2.76 | 3.409 (2) | 123 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−1, y, z−1; (iii) x, y, z−1; (iv) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by VLIR-UOS grant ZEIN2014Z182 to L. Van Meervelt.
References
- Bondarev, D., Zedník, J., Šloufová, I., Sharf, A., Procházka, M., Pfleger, J. & Vohlídal, J. (2010). J. Polym. Sci. A, 48, 3073–3081.
- Bruker (2013). SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2014). APEX2 and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Eweiss, N. F., Bahajaj, A. A. & Elsherbini, E. A. (1986). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 23, 1451–1458.
- Giri, S., Singh, H., Yadav, L. D. S. & Kahre, R. K. (1978). J. Ind. Chem. Soc. 55, 168–171.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ho, H. A., Boissinot, M., Bergeron, M. G., Corbeil, G., Doré, K., Boudreau, D. & Leclerc, M. (2002). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41, 1548–1551. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Knight, P. D., Demauriac, R. A. & Graham, P. A. (1978). Ger. Offen. 2811025.
- Knight, P. D., Demauriac, R. A. & Graham, P. A. (1979) Chem. Abstr. 90, 79146s.
- Mazzone, G., Bonina, F., Arrigo Reina, R. & Blandino, G. (1981). Farmaco, 36, 181–196. [PubMed]
- McKinnon, J. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2007). Chem. Commun. pp. 3814. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mekuskiene, G., Gaidelis, P. & Vainilavicius, P. (1998). Pharmazie, 53, 94–98. [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M. G., Cheng, C. C., Lin, Y. C., Huang, C. W., Lu, F. H., Chang, F. C. & Kuo, S. W. (2014). RSC Adv. 4, 21830–21839.
- Sahin, G., Palaska, E., Kelicen, P., Demirdamar, R. & Altmok, G. (2001). Arzneim.-Forsch. 51, 478–484. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, A. K., Bajaj, O. P. & Chandura, U. J. (1978). J. Ind. Chem. Soc, 55, 962–964.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Singh, H., Yadav, L. D. S. & Bhattacharya, B. K. J. (1979). J. Ind. Chem. Soc. 56, 1013–1017.
- Spackman, M. A. & Jayatilaka, D. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 19–32.
- Vu Quoc, T., Nguyen Ngoc, L., Nguyen Tien, C., Thang Pham, C. & Van Meervelt, L. (2017). Acta Cryst. E73, 901–904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wujec, M., Pitucha, M., Dobosz, M., Kosikowska, U. & Malm, A. (2004). Acta Pharm. 54, 251–260. [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018007193/zp2029sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018007193/zp2029Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018007193/zp2029Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1843042
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report







