Figure 4.
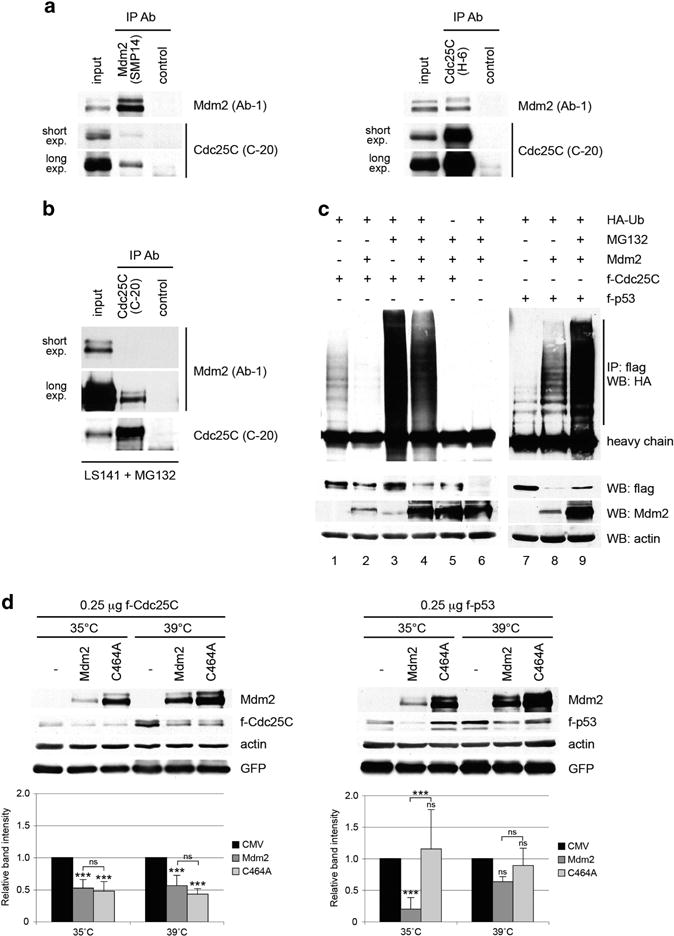
Mdm2 interacts with Cdc25C protein and promotes its ubiquitin-independent degradation. (a) H1299 cells were co-transfected with 1.5 μg of pCMV-flag-Cdc25C and 1.5 μg of pCMV-flag-C464A-Mdm2 mutant. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-Mdm2, anti-Cdc25C or a non-related antibody. Mdm2 and Cdc25C in the immunoprecipitates were detected by immunoblotting. (b) LS141 cells were treated with 10 μM MG132 for 4 h and cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-Cdc25C or a non-related antibody. Mdm2 and Cdc25C in the immunoprecipitates were detected by immunoblotting. (c) H1299 cells were co-transfected with the indicated plasmids and treated as described in Materials and Methods. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-flag and immunoblotted with anti-HA antibodies. (d) Duplicated dishes of murine ts20 cells were transfected with 250 ng of pCMV-flag-Cdc25C or pCMV-flag-p53, 500 ng of pCMV-Mdm2 and 500 ng of pCMV-GFP expression plasmids. Three hours after transfection, one set of dishes was maintained at 35°C and the other placed at 39 °C for 24 h. Cell extracts were immunoblotted with human specific Cdc25C, p53 and Mdm2 antibodies, as well as actin and GFP antibodies. The indicated values are the average of three to five independent experiments. Error bars represent s.d. Statistical analysis corresponds to two-way ANOVA. Notations above error bars correspond to differences with respect to the CMV control. Differences between Mdm2 and C464A transfected samples are marked with brackets (***P<0.001, ns P>0.05).
