Figure 2.
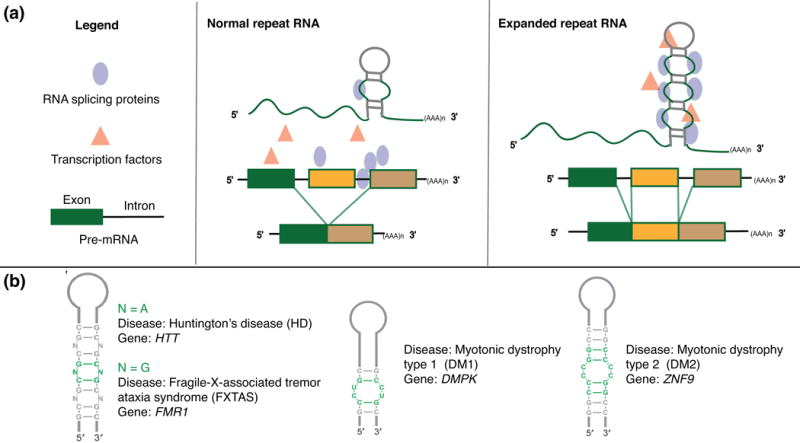
The RNA processing effect induced by expanded repeats and representative structures of single expansions in select diseases. (a) In normal repeat RNA, splicing proteins and transcription factors are available for proper processing to mature mRNA isoforms. When repeats are expanded in disease, proteins needed for efficient splicing are sequestered, leading to excess of mis-spliced mRNA isoforms. Adapted from Todd and Paulson, 2010.70 (b) Secondary structures of repeat RNA and their associated diseases. Adapted from Blaszczyk et al, 2017.71 Abbreviations: N, nucleotide; HTT, Huntington gene; FMR1, Fragile X mental retardation 1; DMPK, DM1 protein kinase; ZNF9, Zinc finger protein 9.
