Figure 4.
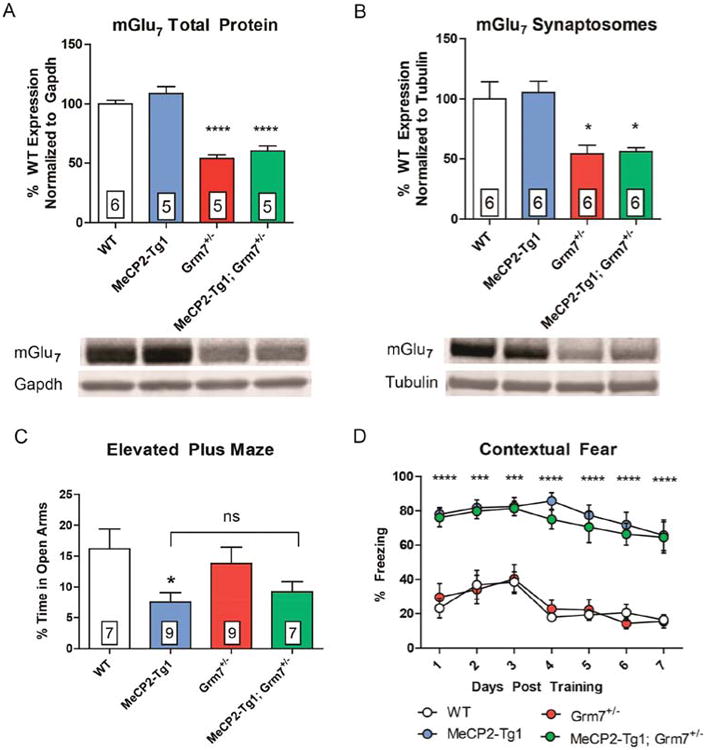
Genetic reduction of mGlu7 does not affect anxiety or fear behavior in MeCP2-Tg1 mice. (A) mGlu7 expression in total protein isolates from hippocampal tissue in MeCP2-Tg1 mice compared relative to WT (WT 100.0 ± 3.1%, MeCP2-Tg1 108.6 ± 5.8%, Grm7+/- 54.0 ± 3.0%, MeCP2-Tg1; Grm7+/− 60.2 ± 4.5%, N = 5–6 mice per genotype, ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni comparisons relative to WT). (B) mGlu7 expression from synaptosomal isolates from hippocampal tissue (WT 100.0 ± 14.1, MeCP2-Tg1 105.3 ± 9.3, Grm7+/− 54.2 ± 7.3, MeCP2-Tg1; Grm7+/− 55.8 ± 3.7, N = 6 mice per genotype, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni comparisons relative to WT). (C) MeCP2-Tg1 mice spend less time in the open arms of an elevated plus maze relative to WT mice, regardless of Grm7 genotype (N = 7–9 mice per genotype, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni comparisons). (D) MeCP2-Tg1 mice exhibit increased contextual fear freezing compared to those that do not, regardless of Grm7 genotype (N = 7–10 mice per genotype, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni comparisons to WT).
