Fig. 7.
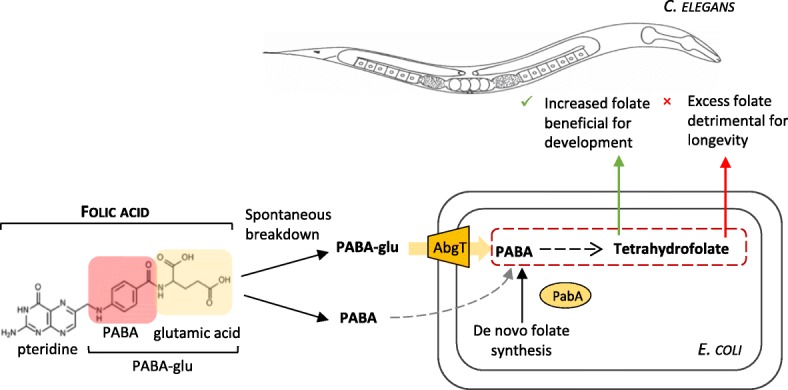
Schematic of the impact of folic acid supplementation on C. elegans via indirect uptake of breakdown products by E. coli. Folic acid is not taken up well by C. elegans directly. We find that the major uptake of folic acid by C. elegans is dependent on its breakdown into PABA-glu and uptake by the E. coli AbgT transporter. This route increases bacterial folate synthesis in both WT and ΔpabA mutant E. coli. Under conditions of folate deficiency (ΔpabA mutant E. coli), increasing bacterial folate via this route is beneficial for C. elegans development. During C. elegans adulthood, this route has a negative impact on longevity as it promotes a bacterial folate-dependent toxicity
